Get started with full observability (cloud native full stack deployment)
This page provides instructions on installing Dynatrace Operator with cloud native full stack configuration to a Kubernetes cluster.
Before you begin
Before installing Dynatrace on your Kubernetes cluster, ensure that you meet the following requirements:
- Your
kubectlCLI is connected to the Kubernetes cluster that you want to monitor. - You have sufficient privileges on the monitored cluster to run
kubectloroccommands.
Cluster setup and configuration
-
You must allow egress for Dynatrace pods (default: Dynatrace namespace) to your Dynatrace environment URL.
-
For OpenShift Dedicated, you need the cluster-admin role.
-
Helm installation Use Helm version 3.
Supported versions
See supported Kubernetes/OpenShift platform versions and distributions.
By default, Dynatrace Operator injects OneAgent in all namespaces, but you can configure it to monitor only specific namespaces and exclude others. For details, see Configure monitoring for namespaces and pods.
Configuring SCC is required for OpenShift for cloudNativeFullStack and applicationMonitoring with CSI driver deployments.
Installation options
Choose one of the installation methods that best suits your needs.
Guided (Dynatrace UI)
Dynatrace version 1.290+
-
Go to Kubernetes or Kubernetes Classic (latest Dynatrace).
-
Select Connect automatically via Dynatrace Operator in the header of the Kubernetes cluster page.
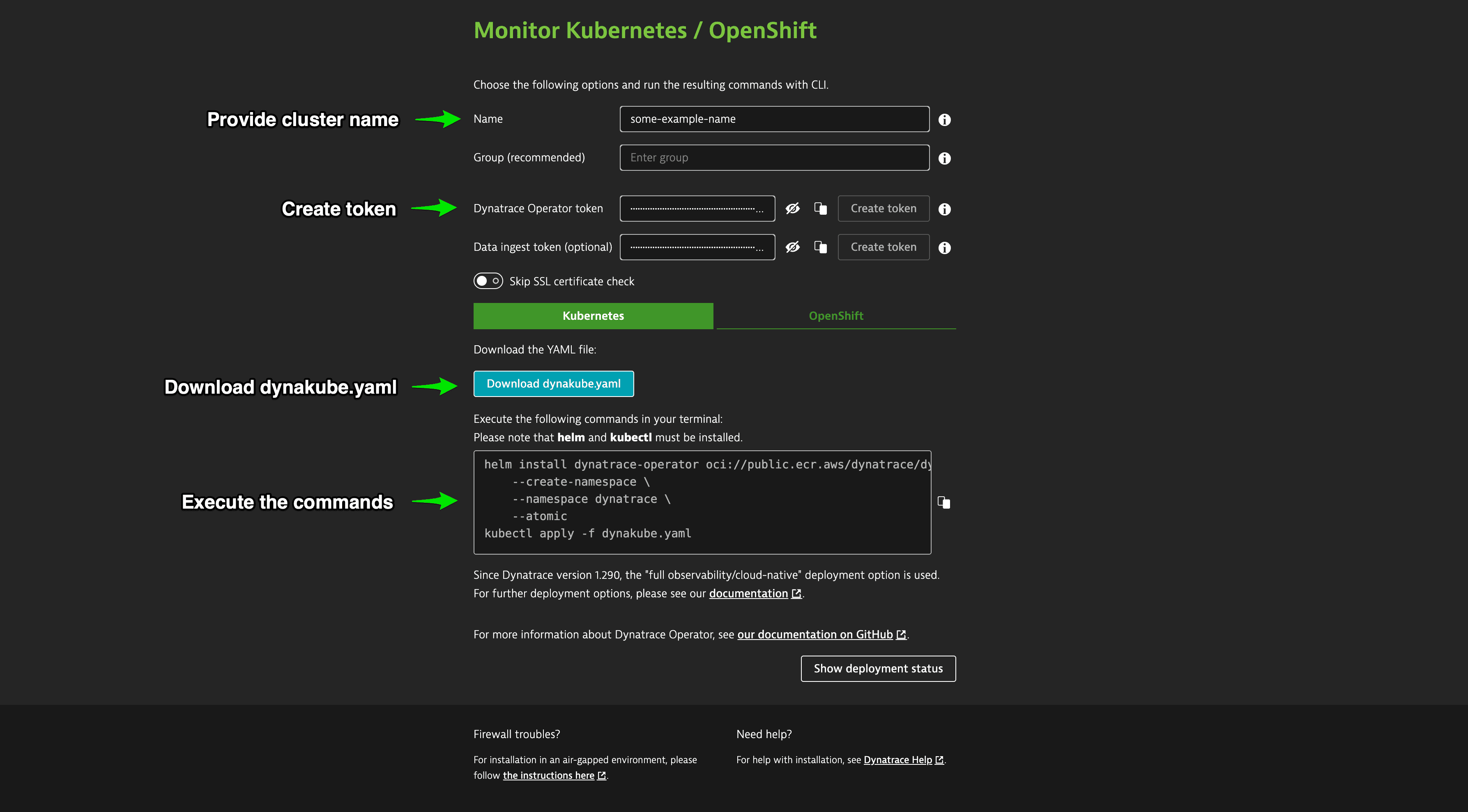
-
Enter the following details.
-
Name: Defines the display name of your Kubernetes cluster within Dynatrace. Additionally, this name will be used as a prefix for naming Dynatrace-specific resources inside your Kubernetes cluster, such as DynaKube (custom resource), ActiveGate (pod), OneAgents (pods), and as a name for the secret holding your tokens.
-
recommended Group: Defines a group used by various Dynatrace settings, including network zone, ActiveGate group, and host group. If not set, defaults or empty values are used.
-
Dynatrace Operator token: Select Create token or enter the API token you previously created. For more information, see Access tokens and permissions.
-
optionalData ingest token: Select Create token or enter the API token you previously created. For more information, see Access tokens and permissions.
-
-
optional Decide whether you want the Dynatrace Operator to disable the verification of the Dynatrace SSL certificate.
This is relevant if you are using Dynatrace Managed with self-signed certificates.
-
Select Download dynakube.yaml. Copy the code block created by Dynatrace created and run it in your terminal. Ensure you execute the commands in the same directory where you downloaded the YAML or adapt the command to link to the location of the YAML manifest.
The downloaded YAML file is a basic version of the DynaKube custom resource definition. To adjust values to your specific needs, refer to the DynaKube custom resource samples for cloud native full stack from GitHub. For more information about all configuration options, see DynaKube parameters for Dynatrace Operator.
-
optional Verify that your DynaKube is running and all pods in your Dynatrace namespace are running and ready.
> kubectl get dynakube -n dynatraceNAME APIURL STATUS AGEdynakube https://<ENVIRONMENTID>.live.dynatrace.com/api Running 45sIn a default DynaKube configuration, you should see the following pods:
> kubectl get pods -n dynatraceNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEdynakube-activegate-0 1/1 Running 0 50sdynakube-oneagent-b88rn 1/1 Running 0 50sdynakube-oneagent-m5jm4 1/1 Running 0 50sdynakube-oneagent-qhd9u 1/1 Running 0 50sdynatrace-oneagent-csi-driver-qxfwx 4/4 Running 0 2m49sdynatrace-oneagent-csi-driver-xk5c4 4/4 Running 0 2m49sdynatrace-oneagent-csi-driver-mz6ch 4/4 Running 0 2m49sdynatrace-operator-7dc8dc7d8c-wmh4z 1/1 Running 0 2m59sdynatrace-webhook-7bb6957fb5-l8fsq 1/1 Running 0 2m59sdynatrace-webhook-7bb6957fb5-rqnqk 1/1 Running 0 2m59sAs OneAgent and CSI-driver are deployed as DaemonSet you should have a OneAgent and CSI-driver pod on each node.
Helm
Dynatrace Operator version 0.8.0+
New Helm installation and upgrade instructions use our Helm chart available from an OCI registry. Therefore, if the Dynatrace repository is currently added to your local Helm repositories, it can be safely removed.
helm repo remove dynatrace
The installation process is independent of whether you are using Kubernetes or OpenShift. The platform is auto-detected during the installation.
-
Install Dynatrace Operator
The following command works for both default installations and installations using an OCI registry.
helm install dynatrace-operator oci://public.ecr.aws/dynatrace/dynatrace-operator \--create-namespace \--namespace dynatrace \--atomic \-f values.yamlEdit the
values.yaml sample from GitHub, and then run the install command, passing the YAML file as an argument:helm install dynatrace-operator oci://public.ecr.aws/dynatrace/dynatrace-operator \--create-namespace \--namespace dynatrace \--atomic \-f values.yamlFor cloud native, full stack deployments, a CSI driver is mandatory. If
installCRDis set tofalse, you need to create the custom resource definition manually before starting the Helm installation:kubectl apply -f https://github.com/Dynatrace/dynatrace-operator/releases/download/v1.1.0/dynatrace-operator-crd.yaml-
For VMware Tanzu Kubernetes (TGKI)
For VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition (formerly PKE), you need to set the
csidriver.kubeletPathvalue invalues.yamlto/var/vcap/data/kubelet/.csidriver:enabled: truekubeletPath: "/var/vcap/data/kubelet" -
For IBM Kubernetes Service (IKS)
Dynatrace Operator version 0.9.0+
For IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service (IKS), you need to set the
csidriver.kubeletPathvalue invalues.yamlto/var/data/kubelet.csidriver:enabled: truekubeletPath: "/var/data/kubelet"
-
-
Create secret for Access tokens
Create a secret named
dynakubefor the Dynatrace Operator token and data ingest token obtained in Tokens and permissions required.kubectl -n dynatrace create secret generic dynakube --from-literal="apiToken=<OPERATOR_TOKEN>" --from-literal="dataIngestToken=<DATA_INGEST_TOKEN>" -
Apply the DynaKube custom resource
Download the DynaKube custom resource sample for cloud native full stack from GitHub. In addition, you can review the available parameters or how-to-guides, and adapt the DynaKube custom resource according to your requirements.
Run the command below to apply the DynaKube custom resource, making sure to replace
<your-DynaKube-CR>with your actual DynaKube custom resource file name. A validation webhook will provide helpful error messages if there's a problem.kubectl apply -f <your-DynaKube-CR>.yaml -
optional Verify deployment
Verify that your DynaKube is running and all pods in your Dynatrace namespace are running and ready.
> kubectl get dynakube -n dynatraceNAME APIURL STATUS AGEdynakube https://<ENVIRONMENTID>.live.dynatrace.com/api Running 45sIn a default DynaKube configuration, you should see the following pods:
> kubectl get pods -n dynatraceNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEdynakube-activegate-0 1/1 Running 0 50sdynakube-oneagent-b88rn 1/1 Running 0 50sdynakube-oneagent-m5jm4 1/1 Running 0 50sdynakube-oneagent-qhd9u 1/1 Running 0 50sdynatrace-oneagent-csi-driver-qxfwx 4/4 Running 0 2m49sdynatrace-oneagent-csi-driver-xk5c4 4/4 Running 0 2m49sdynatrace-oneagent-csi-driver-mz6ch 4/4 Running 0 2m49sdynatrace-operator-7dc8dc7d8c-wmh4z 1/1 Running 0 2m59sdynatrace-webhook-7bb6957fb5-l8fsq 1/1 Running 0 2m59sdynatrace-webhook-7bb6957fb5-rqnqk 1/1 Running 0 2m59sAs OneAgent and CSI-driver are deployed as DaemonSet you should have a OneAgent and CSI-driver pod on each node.
Manifest
Learn more
After you've successfully installed Dynatrace Operator, you may find the following resources helpful for further learning and troubleshooting.
Get actionable answers
Start to analyze your Kubernetes clusters and containerized Apps with Dynatrace and benefit from actionable answers.
Guides
Learn how you can configure Dynatrace Operator to support specific use cases.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshoot any challenges you may encounter while working with the Dynatrace Operator and its various components.
How it works
Want to learn more about the Dynatrace components in your Kubernetes cluster?
Reference
API reference and configuration options for all Dynatrace components within your Kubernetes cluster.
Dynatrace Operator release notes
See release notes for Dynatrace Operator.
Update or uninstall
This page provides a detailed instructions on how to update and uninstall Dynatrace Operator.

