Monitor AWS Fargate
To deploy OneAgent on AWS Fargate, read the instructions provided below.
Prerequisites
- Create an API token in your Dynatrace environment and enable the following permissions:
- Access problem and event feed, metrics, and topology (API v1)
- PaaS integration - Installer download
- Review the list of supported applications and versions.
Integrate OneAgent into your application image
There are three ways to integrate OneAgent with AWS Fargate applications.
Automatic injection EKS
With automatic injection you can manage upgrades and lifecycle.
Kubernetes version 1.20+
On AWS Fargate, only the applicationMonitoring deployment without the CSI driver is supported.
Before you start installation, make sure you have a running AWS Fargate cluster. For details, see Getting started with AWS Fargate using Amazon EKS.
-
Add a Fargate profile to define the Dynatrace Operator deployment.
Be sure it matches the
dynatracenamespace where Dynatrace Operator will be deployed. -
Create a
dynatracenamespace.kubectl create namespace dynatrace -
Install Dynatrace Operator.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/Dynatrace/dynatrace-operator/releases/download/v1.0.1/kubernetes.yaml -
Create the secret holding the API token for authentication to the Dynatrace cluster.
Be sure to replace
<API_TOKEN>with your own value.kubectl -n dynatrace create secret generic dynakube --from-literal="apiToken=<API_TOKEN>" -
Download the preconfigured DynaKube custom resource sample file from GitHub.
-
Review the available parameters, and adapt the DynaKube custom resource according to your requirements.
-
Apply the DynaKube custom resource.
kubectl apply -f applicationMonitoring.yaml
Build-time injection EKS and ECS
With build-time injection you can embed OneAgent into your container image.
Runtime injection ECS
With runtime injection you can pull OneAgent when the container starts. To install Dynatrace OneAgent at runtime, you must deploy your application using a task with two container definitions. One is for downloading and unzipping the OneAgent to a shared volume, the other is your application container, which must mount the same volume.
For the runtime injection, follow the steps below.
-
Go to Fargate Task Definition > Create New Task Definition > select Fargate > click Next Step.
-
Name the task, optionally set roles and sizes, then scroll down to Volumes > Add volume. Add a volume of type
Bind Mountnamedoneagent.You must create a volume before creating container definitions in order to set the shared volume in each container.
-
Scroll up to Container Definition > choose Add container, and in the Standard subsection, add a container named
install-oneagent, set the image to Alpine version 3.8+ ("alpine:3"), and select the memory limits.There are two types of memory limits: soft and hard. ECS requires that you define the limit for at least one type of memory. We recommend using the default setting (soft limit of 128 MiBs), as it's less restrictive, but you can adjust it as needed.
-
Scroll to Environment and do the following:
-
Uncheck the Essential parameter.
-
In the Entry point field, enter
/bin/sh,-c. -
In the Command field, enter
ARCHIVE=$(mktemp) && wget -O $ARCHIVE "$DT_API_URL/v1/deployment/installer/agent/unix/paas/latest?Api-Token=$DT_PAAS_TOKEN&$DT_ONEAGENT_OPTIONS" && unzip -o -d /opt/dynatrace/oneagent $ARCHIVE && rm -f $ARCHIVE.
-
-
In the Environment variables subsection, define:
-
DT_API_URL- this is the API URL for your Dynatrace environment.- For SaaS:
https://<your-environment-id>.live.dynatrace.com/api - For Managed:
https://<cluster>/e/<your-environment-id>/api - For ActiveGate:
https://<your-active-gate-IP-or-hostname>:9999/e/<your-environment-id>/api.
- For SaaS:
-
DT_ONEAGENT_OPTIONS- this is the flavor (valid options aredefaultormuslfor Alpine images) and the technology (code module).- Syntax for
defaultisflavor=default&include=all. - Syntax for
muslisflavor=musl&include=all.
- Syntax for
-
DT_PAAS_TOKEN- this is your PaaS token to download the OneAgent code modules.
-
-
Scroll to Storage and logging to define the mount point with the source volume
oneagentand the container path/opt/dynatrace/oneagent. -
Click Add to create the container definition.
-
Choose Add container again, this time to define your application, and complete the fields in the Standard subsection according to your application requirements.
-
Scroll to Environment, and in Environment variable, define
LD_PRELOADwith the value/opt/dynatrace/oneagent/agent/lib64/liboneagentproc.so. -
Scroll to Startup Dependency Ordering and enter the container name
install-oneagentand the conditionComplete. -
Scroll to Storage and logging to define the mount point with the source volume
oneagentand the container path/opt/dynatrace/oneagent. -
Select Update to update your container definition.
-
Deploy the new version of your task definition on your ECS cluster.
- For the
install-oneagentcontainer, you can see the code modules' ZIP file being downloaded by wget and being unzipped. For your application workload container, you can see the code module being loaded by the process.
In Dynatrace, your Fargate application workload container will show up in the Hosts section. The instrumented process will show up in Processes as a typical Docker container.
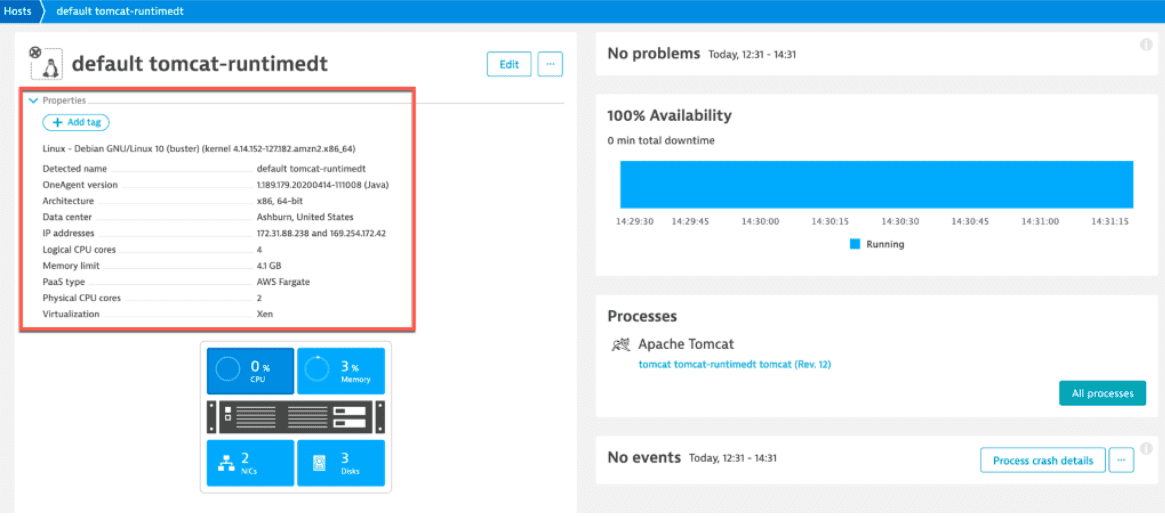
The runtime approach requires Fargate version 1.3+. For earlier versions, select the build-time approach.
Configure network zones optional
You can configure network zones as an environment variable:
DT_NETWORK_ZONE: equalsyour.network.zone
See network zones for more information.
Monitoring consumption
For AWS Fargate, monitoring consumption is based on host units. To learn how host units are calculated for Dynatrace application and infrastructure monitoring, see Application and Infrastructure Monitoring (Host Units).