If you have your applications running on AWS or a similar cloud-based solution, you’ve effectively “outsourced” your networking to the cloud as well. Of course, this can be of great value. Most significantly because it frees you from maintaining physical network infrastructure. Not having physical access to your network doesn’t, however, mean that you’re free from taking care of your network. Let’s see why you need network monitoring in the cloud.
A bit of history
In traditional application architectures, network infrastructure was kept under the strict control of network teams. These teams were responsible for upgrading overloaded equipment before problems arose, identifying and replacing weak network links, resolving bottlenecks, observing latency metrics and delayed data delivery, and even detecting security threats. In other words, traditional network teams looked after all seven OSI layers.
Modern architectures need more networking than ever
In cloud-based architectures, the situation is different and the network has become even more important. Let’s imagine a typical cloud-based architecture situation. You run a datacenter with a flexible number of allocated computing instances (for example, due to the pricing model and volatile demands for CPU). Your datacenter serves distributed applications that are backed by, for example, microservices. Additionally, let’s say that your applications are distributed via Docker containers to give your DevOps teams some flexibility. In situations like this, you need more networking than ever. Your network must shoulder all the communications required between the microservices. It serves as a virtual nervous system for your applications.
Even though the network is not physically available to system administrators, it still exists and requires attention. It’s often difficult to know where exactly your machines are physically hosted and how they’re connected with other hosts in your network. Related virtual machines and services can even be hosted on the same virtual host, in which case your network exists only as a memory read operation. This means, the physical network very often coexists with multiple virtual networks.
Challenges in cloud-based networks
The inability to physically access a network (OSI layers 1-2) makes it hard for DevOps teams to keep an eye on it. They can use the monitoring tools offered by their cloud provider, for example Cloud Watch, to fetch network metrics like NetworkIn and NetworkOut, but these metrics can be insufficient in detecting network problems.
Here are some of the key challenges that DevOps faces in maintaining virtual network performance:
- Competing processes for network resources (for example, the TCP Incast problem)
- Variable network infrastructure through new or stopped instances
- Scalability of network load via elastic network interfaces
- Quality of connections inside your data center
- Quality of connections to private networks outside your data center
Monitoring network usage
Your network monitoring must be able to react to infrastructure changes such as mentioned above. In particular, it needs to be able to handle virtual network interfaces. Hence, your monitoring needs to run on your hosts and consistently keep watch for changes of your virtual infrastructure. From this position it can observe network connections between processes that communicate with other processes and services, thereby monitoring actual network usage instead of just network devices.
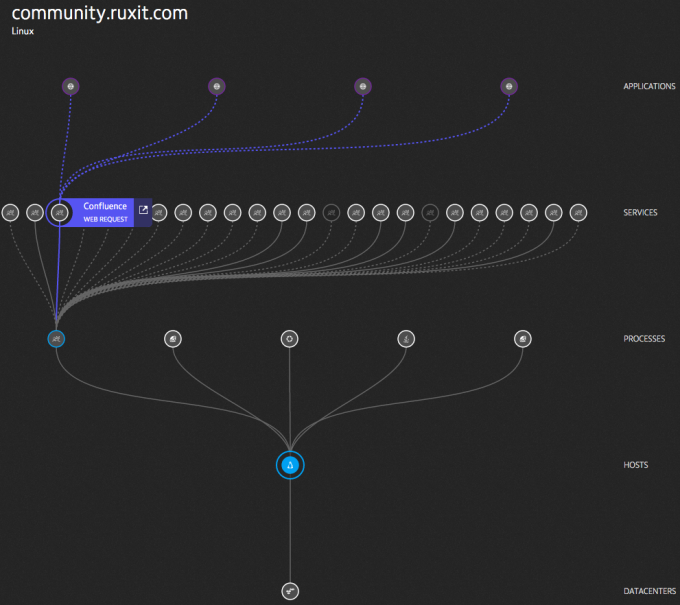
Resource monitoring is key… and simple!
With this monitoring approach, your network won’t be seen simply as a collection of network interfaces, routing tables, and security groups. Rather your network will be viewed as a limited resource used by processes and applications. This resource can be monitored along with CPU, memory, and storage, and even measured at the process level. This enables full-stack application performance monitoring and the ability to trace network problems all the way up to the application level.
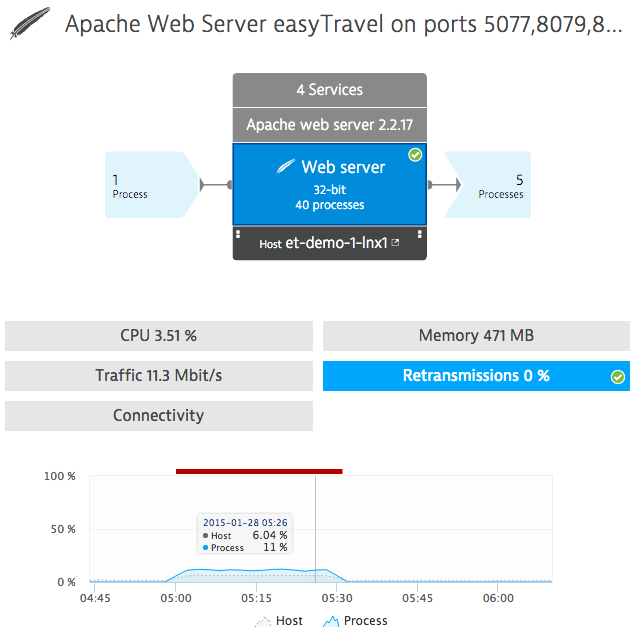
There are a few basic network performance metrics you should keep in mind:
- The traffic of network data (throughput) is the basic indicator for network performance.
- The Connectivity metric provides the percentage of successfully established TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connections and indicates accessibility of services. TCP connections may be refused or end up in timeouts, so connectivity is a good indicator of network problems between sender and receiver.
- With respect to the quality of established TCP connections, the retransmission rate is also worth monitoring. The TCP protocol is a reliable and error-checked protocol. This means the receiver must confirm the packets sent over a network link; otherwise, they are considered lost and then retransmitted by the sender. Therefore, retransmission rate is a good indicator of poor network links and overloaded network infrastructure.
The bottom line is that you shouldn’t blindly trust cloud providers regarding the health of your “outsourced” virtual network infrastructure. Virtualized networks cannot be monitored in a more or less traditional manner. They should at least be monitored from the point of view of your hosts and processes so that you have some meaningful network performance indicators.



Looking for answers?
Start a new discussion or ask for help in our Q&A forum.
Go to forum