As global warming advances, growing IT carbon footprints are pushing energy-efficient computing to the top of many organizations’ priority lists. Energy efficiency is a key reason why organizations are migrating workloads from energy-intensive on-premises environments to more efficient cloud platforms. But while moving workloads to the cloud brings overall carbon emissions down, the cloud computing carbon footprint itself is growing.
“The cloud now has a greater carbon footprint than the airline industry,” wrote anthropologist Steven Gonzalez Monserrate in a 2022 article from MIT. “A single data center can consume the equivalent electricity of 50,000 homes.” The growing adoption of innovations like generative AI, based on large-language models (LLMs), will only increase demand for cloud computing. This adoption will further impact carbon emissions. Research from 2020 suggests that training a single LLM generates around 300,000 kg of carbon dioxide emissions—equal to 125 round-trip flights from New York to London.
Does that mean the answer is to slow the growth of AI or cloud technologies more broadly? Given the benefits of these innovations, organizations can’t afford to pull back on their efforts to build AI and shift more workloads to the cloud. However, organizations can turn to innovative solutions to improve their energy efficiency by mitigating their cloud computing carbon footprint.
How Dynatrace tracks and mitigates its own IT carbon footprint
Like many tech companies, Dynatrace is experiencing increased demand for its SaaS-based Dynatrace platform, which we host on cloud infrastructure. As we onboard more customers, the platform requires more infrastructure, leading to increased carbon emissions. At the same time, many existing customers are migrating from Dynatrace Managed, our on-premises solution, to our SaaS offering. These migrations add to the Dynatrace cloud computing carbon footprint as we onboard more customers’ observability and security workloads. However, since moving on-premises workloads to the cloud can lower the overall carbon footprint by 80% or more, the result is a net reduction in carbon emissions.
Nonetheless, to help mitigate climate change, it’s critically important for organizations to measure, monitor, and reduce their IT carbon footprints. Certainly, this is true for us. We also recognize that many of our customers have the same need. Many cloud service providers offer tools that measure a subscriber’s cloud computing carbon footprint when using their service. But they don’t measure the carbon footprint of the many apps and infrastructure resources running across that subscriber’s multicloud environments. They also can’t assess the IT carbon footprint of a subscriber’s on-premises apps and infrastructure. That’s why we developed Carbon Impact.
The Carbon Impact app assesses carbon emissions and energy consumption from all monitored hosts. It also provides organizations with actionable guidance for how to reduce their overall IT carbon footprint. Developed using guidance from the Sustainable Digital Infrastructure Alliance (SDIA) and expanding on formulas from the open source project Cloud Carbon Footprint, Carbon Impact measures and reports the IT carbon footprint of all Dynatrace-monitored hosts across an organization’s entire hybrid and multicloud environment in a single interface.
Assessing our baseline cloud computing carbon footprint
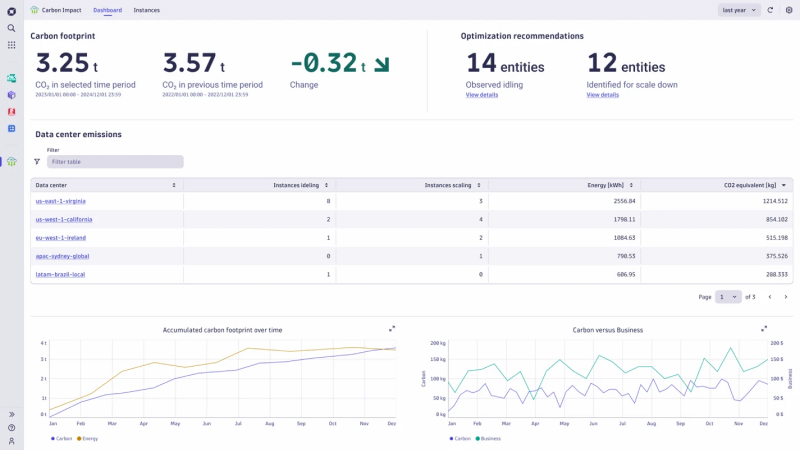
Using Carbon Impact, we can assess our baseline carbon footprint with accuracy and granularity that’s nearly impossible to glean from other sources. The app’s advanced algorithms and real-time data analytics translate utilization metrics into their CO2 equivalent (CO2e). These metrics include CPU, memory, disk, and network I/O. This analysis provides us with a holistic view of our multicloud environment’s carbon emissions and identifies major emissions sources. As a result, this baseline measurement has become an important component of our sustainability strategy. It increases our awareness across IT and business stakeholders as we use these insights to build action plans to reduce our emissions and track the results of those efforts.
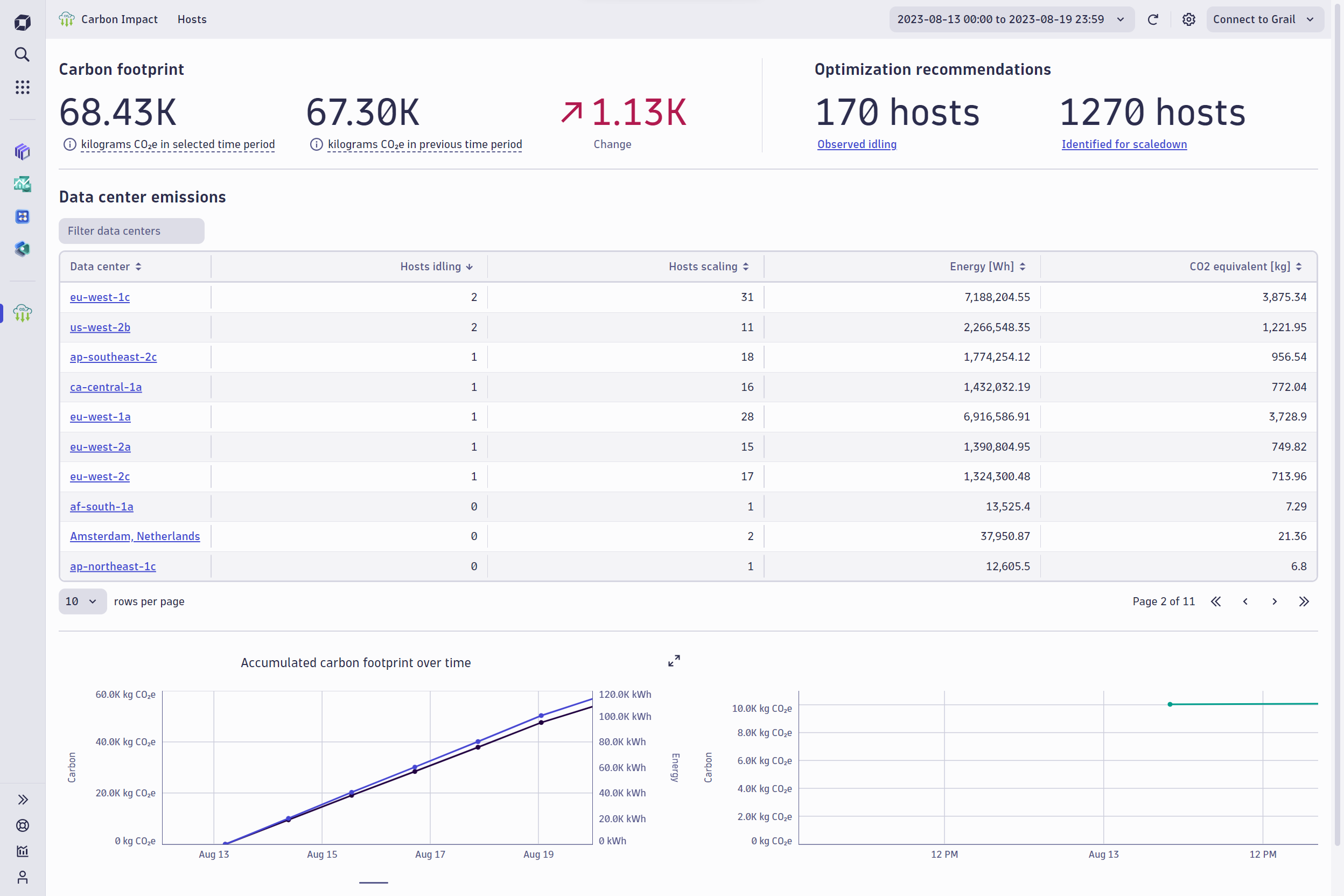
Tracking cloud computing carbon footprint by host
The ‘Hosts’ view details energy and CO2e consumption per host with filters to help narrow the focus to high-impact areas. For example, Dynatrace has been able to view underutilized instances in a specific AWS data center along with top CO2e emitters within a specific host group.
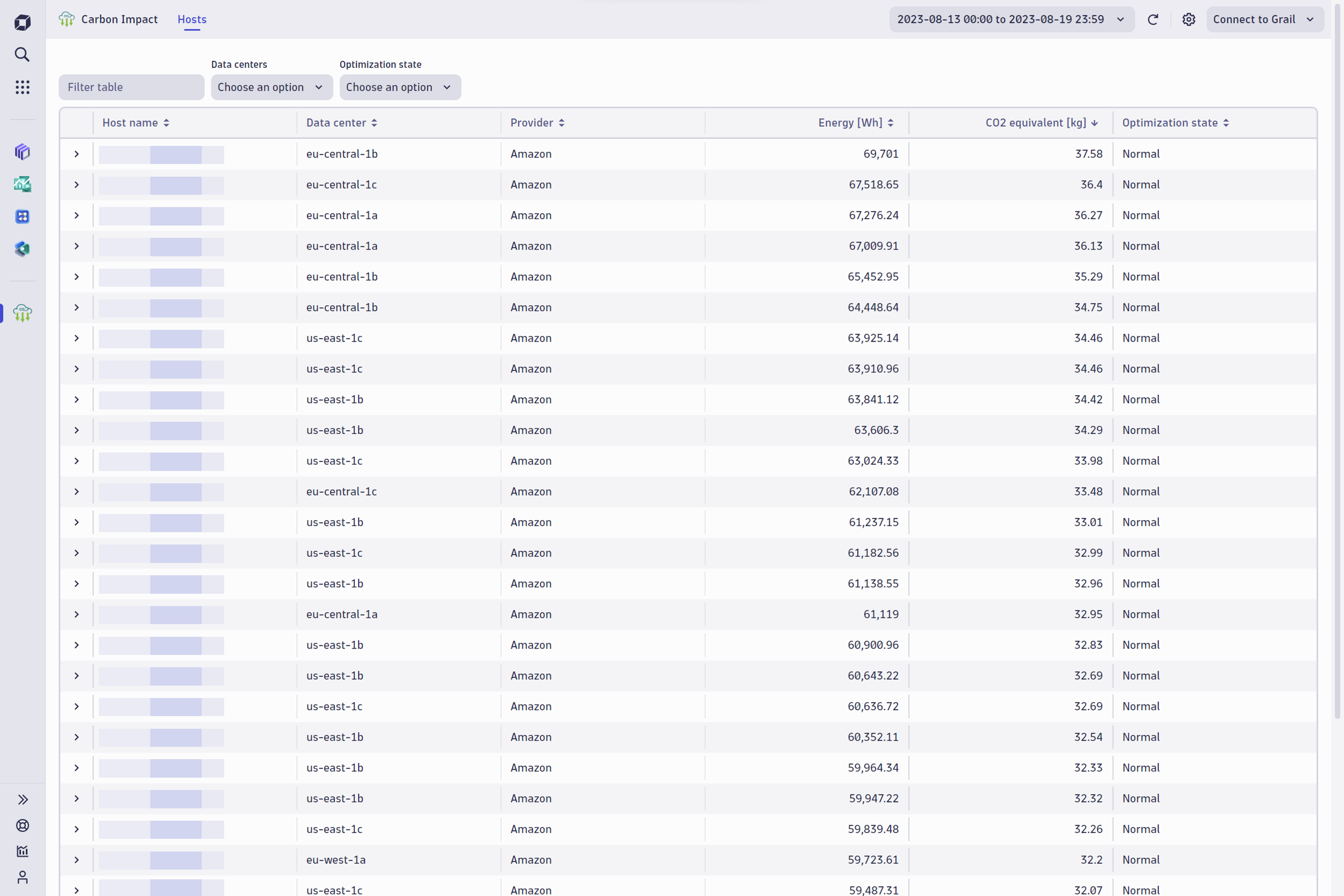
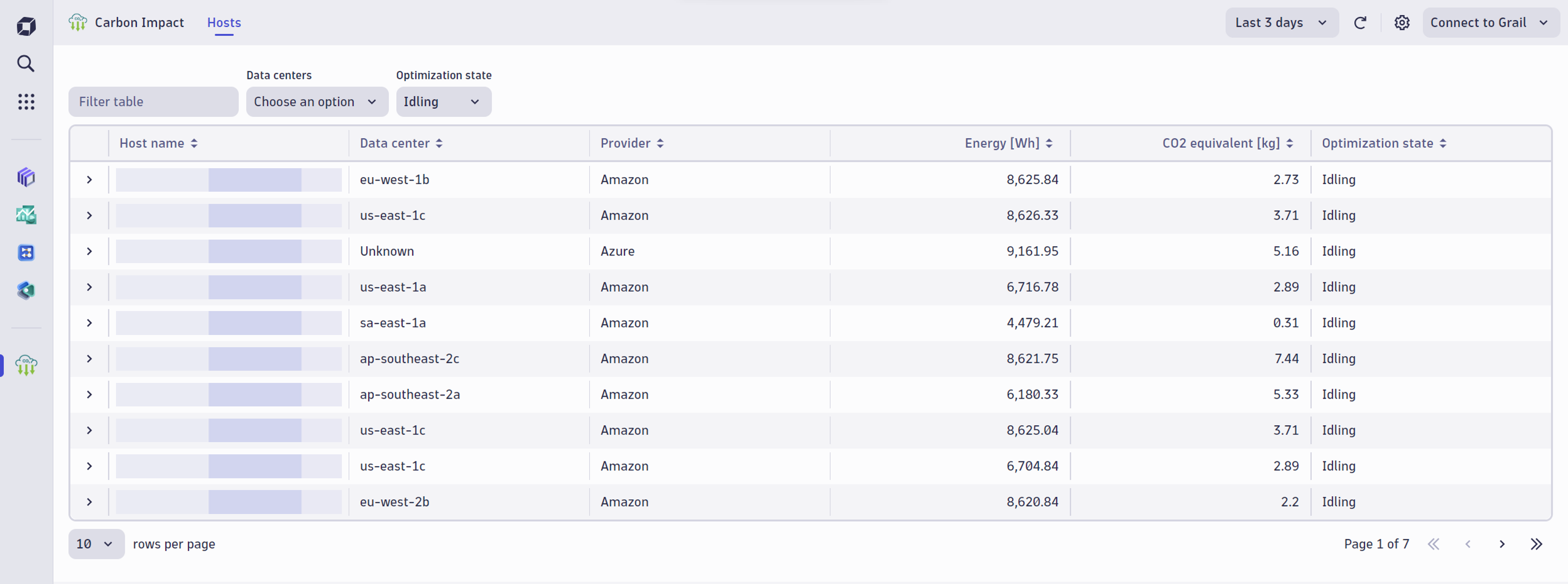
Optimizing host idling and scaling to reduce IT carbon footprint
Carbon Impact automatically reports idle and under-utilized instances as targets for optimization. Because Carbon Impact is integrated with Dynatrace Smartscape® topology modeling, it’s easy to drill into host and process details. Or open a Notebook for ad hoc analysis, giving us insights so we can safely scale down or retire underutilized instances. Using these recommendations, we focused our reduction goals on instances with the highest potential impact, shifting workloads and resizing instances where appropriate.
Helping organizations track their IT carbon footprint to forge a greener future
At Dynatrace, we’re committed to measuring and reducing our own greenhouse gas emissions. By extension, we want to enable our customers to do the same. The Dynatrace unified observability and security platform makes this possible. Carbon Impact is an example of our contribution to making IT more energy-efficient and sustainable for everyone, even as AI is fueling the data explosion.
We built Carbon Impact using Dynatrace AppEngine, which customers and partners can also use to create additional custom, compliant, and intelligent data-driven apps. The AppEngine uses an easy, low-code approach to unlock the wealth of insights available in modern cloud ecosystems, including revealing where organizations consume their energy.
”As Dynatrace looks to the future, considering our environmental impact is more important than ever,” says Thomas Reisenbichler, VP of Site Reliability Engineering at Dynatrace. “We’re confident that Dynatrace will be able to optimize our cloud infrastructure carbon emissions by leveraging the Dynatrace platform for proactive management and orchestration, utilizing our Carbon Impact app to unlock greater optimization potential, and using green coding initiatives to improve performance.”
Using Carbon Impact, we can now implement efficiency measures driven by the app’s benchmarks and recommendations. Because it facilitates ongoing monitoring and tracks progress toward our sustainability goals, we can adjust our strategy to reduce our IT carbon footprint. By integrating sustainability into our growth strategy—and our product offering—Dynatrace is deepening its commitment to responsible business practices, transparency, and a greener future.




Looking for answers?
Start a new discussion or ask for help in our Q&A forum.
Go to forum