Host monitoring (DPS)
Host monitoring consumption varies depending on which OneAgent monitoring mode is in use.
- Dynatrace OneAgent offers Full-Stack Monitoring, Infrastructure Monitoring, and Foundation & Discovery modes for the hosts and containers in your digital infrastructure. To learn more about the OneAgent monitoring modes, see Infrastructure and Discovery monitoring modes.
- For Kubernetes clusters, Dynatrace offers Kubernetes Monitoring.
- Dynatrace provides a dedicated DPS model for Mainframe Monitoring.
Full-Stack Monitoring
Full-Stack Monitoring mode offers comprehensive application performance monitoring, including distributed tracing, code-level visibility, CPU profiling, memory profiling, and deep process monitoring. That is true for hosts and containers. For hosts, all Infrastructure Monitoring functionality is included with Dynatrace Full-Stack Monitoring. A host is defined as a single physical or virtual server or cloud instance running an operating system, whereas a container is defined as an isolated space on a host or any cloud infrastructure for running individual application processes.
A full-stack monitored host has OneAgent installed in Full-Stack Monitoring mode, actively sending data to Dynatrace. Billing of full-stack monitored hosts (whether run in the cloud or on-premises) depends on a host's memory size and the duration a host was monitored by OneAgent.
GiB-hours
Dynatrace uses GiB-hours (referred to as "memory-gibibyte-hours" in your rate card) as the unit of measure for calculating your organization's consumption of host monitoring in Full-Stack Monitoring mode. The more memory that a host has, and the longer that the host is monitored, the higher the number of GiB-hours that the host consumes.
The advantage of the GiB-hour approach to monitoring consumption is its simplicity and transparency. Technology-specific factors (for example, the number of JVMs or the number of microservices hosted on a server) don't affect consumption. It doesn't matter if a host runs .NET-based applications, Java-based applications, or something else. You can have 10 or 1,000 JVMs; such factors don't affect an environment's monitoring consumption.
Billing granularity for GiB-hour consumption
Dynatrace is built for dynamic cloud-native environments where hosts and services are rapidly spun up and destroyed. Therefore, billing granularity for GiB-hour consumption is calculated in four 15-minute intervals per hour. When a host or container is monitored for fewer than 15 minutes in an interval, GiB-hour consumption is rounded up to 15 minutes before consumption is calculated.
GiB-hour calculation for physical hosts and virtual machines (VMs)
Each installed instance of Dynatrace OneAgent running on an operating system instance (deployed on either K8s, a container platform, or a physical or virtual machine) in Full-Stack Monitoring mode consumes GiB-hours based on the monitored host's physical or virtual RAM, calculated in 15-minute intervals (see the diagram example below).
The RAM of each VM or host is rounded to the next multiple of 0.25 GiB (which equates to 256 MiB) before monitoring consumption is calculated. A 4 GiB minimum is applied to GiB-hour consumption for physical and virtual hosts. For example, a host with 8.3 GiB memory is counted as an 8.5 GiB host, being the next multiple of 0.25 GiB, while a host with 2 GiB memory is counted as a 4 GiB host (no rounding needed, but application of the 4 GiB minimum).
GiB-hour calculation for application-only container monitoring
In cloud-native environments, services and hosts are often short-lived. Therefore calculating monitoring consumption in 15-minute time intervals, rather than full hours, better reflects actual usage. Containers, which are an essential mechanism in cloud-native environments, are typically smaller in memory size than hosts. Therefore, the minimum memory threshold for containers is 256 MiB, rather than 4 GiB, the minimum memory threshold for hosts.
The same rounding as for hosts, to the next multiple of 0.25 GiB, also applies to containers. For example, a container with 780 MiB memory is counted as a 1 GiB container (780 MiB, which equals 0.76 GiB, being rounded up to the next multiple of 0.25 GiB).
The diagram below illustrates how memory is counted for GiB-hour consumption calculations at 15-minute intervals.

Figure 1. GiB-hour consumption for hosts and containers is based on memory size, calculated in 15-minute intervals each hour. Each interval is divided by 4 in order to reach the GiB-hour consumption unit of measure.
Used memory logic
Memory-size calculations for containers monitored in an application-only approach are based on each container's used memory.
Memory-size calculations based on a container's used memory require OneAgent version 1.275+ (for Kubernetes containers) or OneAgent version 1.283+ (for other serverless containers).
Older OneAgent versions use the customer-defined memory limit. If no memory limit is set, the memory of the underlying virtual machine is used instead.
Exceptions
For Azure App Services running on the App Service (Dedicated) plan for Windows, instances are counted as hosts and the defined memory of all instances is aggregated to determine total memory—regardless of how many applications run on those instances.
For Azure App Service on Linux and Azure App Service for Linux Containers with OneAgent version 1.283+, memory consumption is calculated using the memory of each plan instance. In these cases, there is no ability to set container resource limits.
Solaris Zones are counted as hosts.
Monitored containers that are not detected as containers are counted as hosts.
Metrics
Full-Stack Monitoring includes all Infrastructure Monitoring metrics, application performance monitoring metrics, and other built-in metrics. In addition, Full-Stack Monitoring includes a fixed number of custom metric data points for each GiB that contributes to your environment's GiB-hour consumption. As of April 26, 2023, Dynatrace offers 900 included custom metric data points for each GiB of host memory, calculated at 15-minute intervals.
Your environment's included metric data points are applied automatically to metrics that originate at hosts and containers that are monitored by OneAgent in Full-Stack Monitoring mode. You will only be billed for consumed metric data points if you exceed your included volume of metric data points.
Included metric datapoints that are not consumed within the 15-minute interval in which they are granted do not roll over to subsequent intervals.
Included metric data point calculation example
Considering the example shown in Figure 1, here are the calculations for the included metric data point volumes for each of the four 15-minute intervals, assuming a volume of 900 included metric data points for each 15-minute interval.
First 15-minute interval
900 (included metric data points) × 13.5 (GiB memory) = 12,150 included metric data points
Second 15-minute interval
900 (included metric data points) × 9.5 (GiB memory) = 8,550 included metric data points
Third 15-minute interval
900 (included metric data points) × 8.75 (GiB memory) = 7,875 included metric data points
Fourth 15-minute interval
900 (included metric data points) × 0.25 (GiB memory) = 225 included metric-data-points
How metric data points are consumed in Full-Stack Monitoring mode
Metric data-point consumption takes many forms. An equal number of data points can be consumed:
By a few high-resolution metrics or numerous low-resolution metrics.
Equally across multiple 15-minute intervals or all at once in a single minute.
By all monitored hosts, a subset of all Full-Stack monitored hosts, or a single host.
Additional metric data points that your environment consumes (beyond those data points that are included with each GiB of memory that contributes to your consumed GiB-hours) are billed as Custom Metrics Classic.
Distributed traces
Full-Stack Monitoring includes Dynatrace PurePath® distributed tracing. OneAgent automatically manages the volume of captured trace data. For details, see Adaptive Traffic Management documentation. The peak trace volume available in an environment at any time depends on how many GiB of memory contribute to your GiB-hour consumption. Every contributing GiB of host memory adds peak trace volume of 45 KiB/min. Each environment has a minimum trace peak volume of 14 MiB/min.. This trace volume is available for all traces sent by OneAgent code modules or via OneAgent Trace API.
Taking the hosts shown in Figure 1 as an example, the peak trace volume for each minute equals the environment minimum (14 MiB/min). For the calculation of trace data volume in this next example, we'll apply a multiplier (100) to host memory size to generate a more realistic scenario. This assumes there are 100 times more GiB contributing within each 15-minute interval.
Peak trace volume/minute calculation example
First 15-minute interval
45 KiB (peak trace volume) × 13.5 (GiB memory) × 100 (example multiplier) = 59.32 MiB/min
Second 15-minute interval
45 KiB (peak trace volume) × 9.5 (GiB memory) × 100 (example multiplier) = 41.75 MiB/min
Third 15-minute interval
45 KiB (peak trace volume) × 8.75 (GiB memory) × 100 (example multiplier) = 38.45 MiB/min
Fourth 15-minute interval
45 KiB (peak trace volume) × 0.25 (GiB memory) × 100 (example multiplier) = 14.00 MiB/min (the minimum trace volume)
Note that traces sent via the Custom Trace API are billed as Custom Traces Classic.
Dynatrace retains the total amount of ingested trace volume from your environment for ten days, with index-level access for 35 days. For an average host with 16 GiB memory, this translates to 10 GiB of retained trace volume (45 Kib per GiB/min × 16 GiB memory × 60 min × 24h × 10 days / 1024 / 1024).
CPU, memory, and thread profiling
Full-Stack Monitoring includes CPU, memory, and thread profiling for technologies like Java, .NET, Go, Node.js, and PHP. OneAgent uses an intelligent patented mechanism to manage the volume of profiling data. Dynatrace retains the total amount of ingested profiling data from your environment for ten days.
Consumption details: Full-Stack
Dynatrace provides built-in usage metrics that help you understand and analyze your organization's consumption of Full-Stack Monitoring. To use these metrics, in Data Explorer, enter DPS in the Search field. These metrics are also available via the Environment API and in Account Management (Usage summary > Full-Stack Monitoring > Actions > View details).
Here are the metrics you can use to monitor the consumption of Dynatrace Full-Stack Monitoring.
- (DPS) Full-Stack Monitoring billing usage
Key:
builtin:billing.full_stack_monitoring.usageDimension: count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Total GiB memory of all hosts monitored in Full-Stack Monitoring mode counted in 15-min intervals.
- (DPS) Full-Stack Monitoring billing usage per host
Key:
builtin:billing.full_stack_monitoring.usage_per_hostDimension: Host (
dt.entity.host)Resolution: 15 min
Description: GiB memory per host monitored in Full-Stack Monitoring mode counted in 15-min intervals.
- (DPS) Full-stack usage by container type
Key:
builtin:billing.full_stack_monitoring.usage_per_containerDimension: application_only_type; k8s.cluster.uid; k8s.namespace.name
Resolution: 15 min
Description: GiB memory per container monitored in Full-Stack application-only Monitoring mode counted in 15-min intervals.
- (DPS) Total metric data points reported by Full-Stack monitored hosts
Key:
builtin:billing.full_stack_monitoring.metric_data_points.ingestedDimension: Count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Number of reported metric data points aggregated over all Full-Stack monitored hosts.
- (DPS) Metric data points reported and split by Full-Stack monitored hosts
Key:
builtin:billing.full_stack_monitoring.metric_data_points.ingested_by_hostDimension: Host (
dt.entity.host)Resolution: 15 min
Description: Number of reported metric data points split by Full-Stack monitored hosts.
- (DPS) Available included metric data points for Full-Stack monitored hosts
Key:
builtin:billing.full_stack_monitoring.metric_data_points.includedDimension: Count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Total number of included metric data points that can be deducted from the consumed metric data points reported by Full-Stack monitored hosts.
- (DPS) Used included metric data points for Full-Stack monitored hosts
Key:
builtin:billing.full_stack_monitoring.metric_data_points.included_usedDimension: Count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Number of consumed included metric data points for Full-Stack monitored hosts.
Monitor memory-GiB-hour consumption for Full-Stack monitored hosts
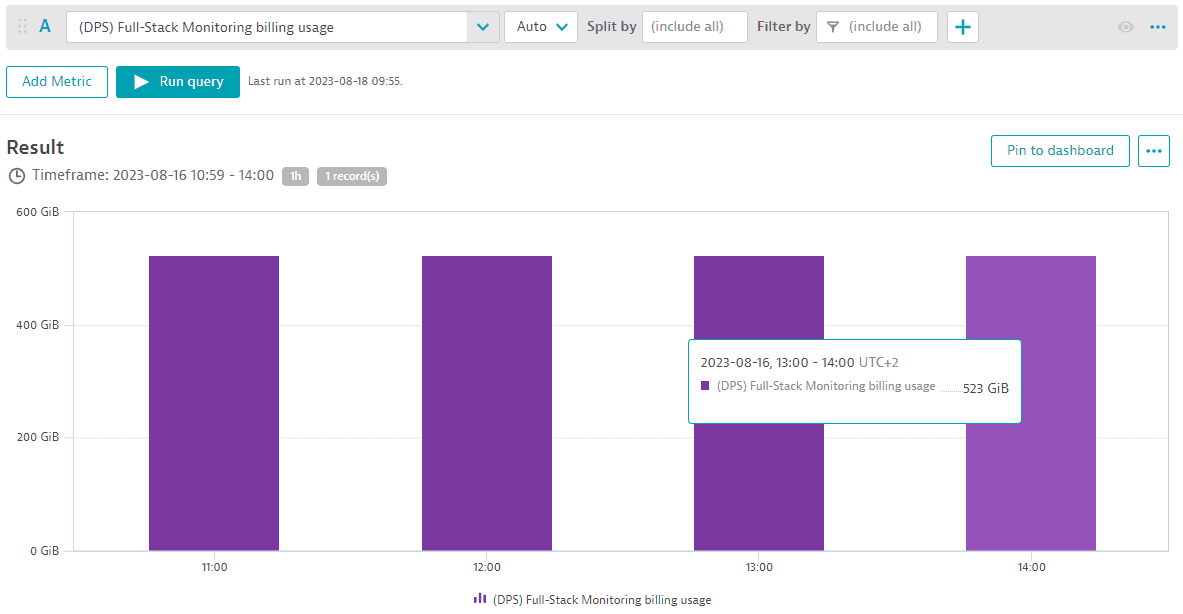
You can monitor the total memory-GiB-hour consumption aggregated across all Full-Stack monitored hosts for different intervals (15 min, hour, day, or week) for any selected timeframe using the (DPS) Full-Stack Monitoring billing usage metric. The example below shows memory GiB monitored in 1-hour intervals. Between 11:00 and 14:00, 523 memory-GiB were monitored each 1 hour. This results in 523 memory-GiB-hours consumed.
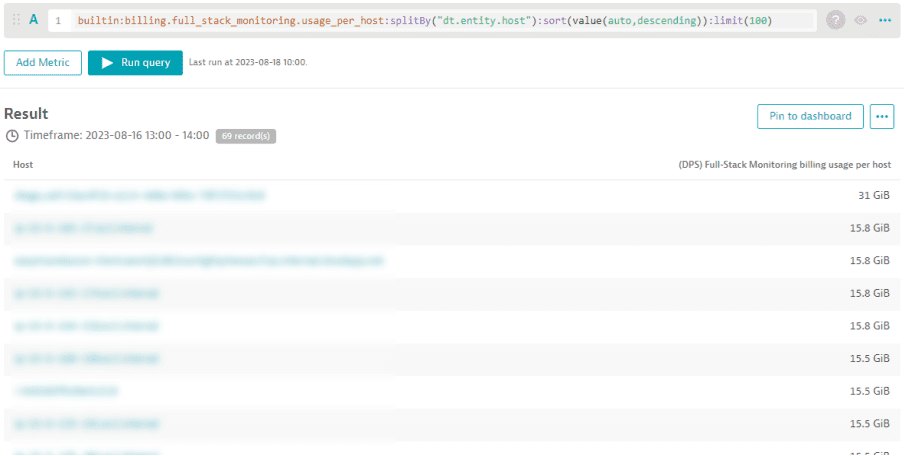
You can break down the total memory-GiB-hour consumption using the (DPS) Full-Stack Monitoring billing usage per host metric. The example below shows the list of all hosts that contributed to the 523 memory-GiB-hour consumption between 13:00 and 14:00. The respective number of memory-GiB-hours per host is displayed as well.
Monitor memory-GiB-hour consumption for Full-Stack monitored containers
Platform and cluster owners can monitor their Kubernetes clusters using Kubernetes Monitoring. Application owners can leverage Full-Stack Monitoring in application-only mode to monitor applications running within Kubernetes clusters.
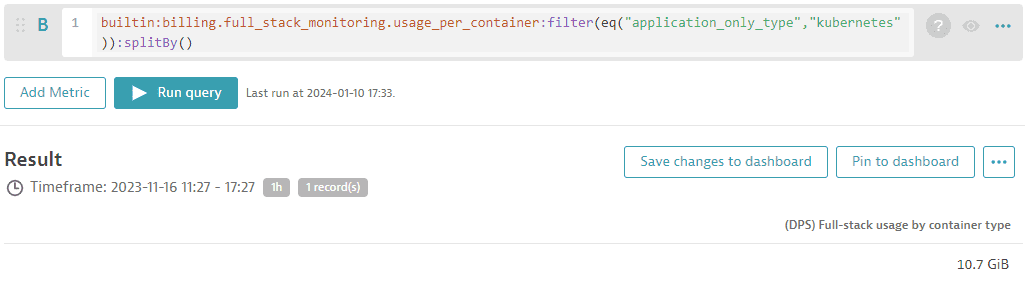
To get consumption insights for monitored Kubernetes clusters or namespaces, you can query memory-GiB-hour consumption by leveraging the (DPS) Full-Stack Monitoring billing usage per container metric, as shown in the following query:
builtin:billing.full_stack_monitoring.usage_per_container:filter(eq("application_only_type","kubernetes")):splitBy()
In the example below, 1.58 TiB of memory was consumed by the Kubernetes cluster within the past 30 days.
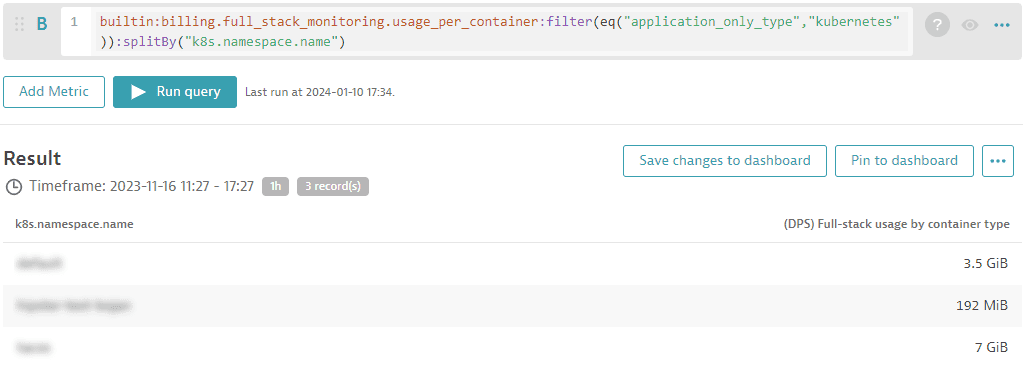
Of course, you can filter your analysis for deeper insights (for example, add a split for Kubernetes namespaces).
Monitor metric consumption for Full-Stack monitored hosts
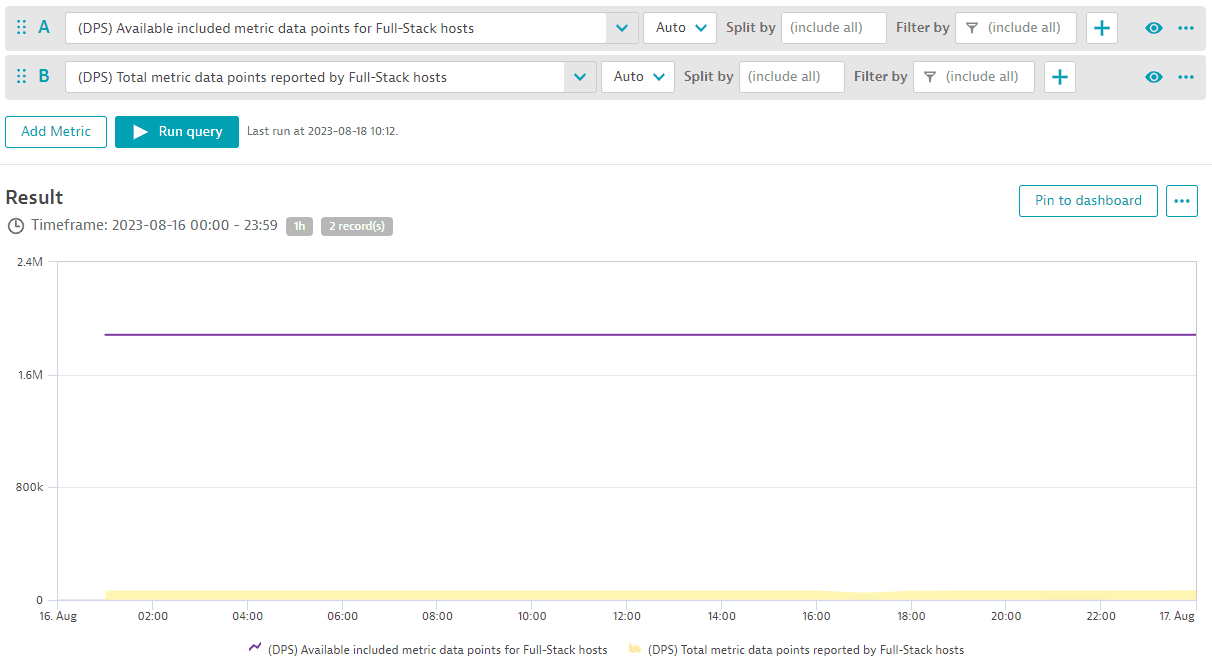
To monitor your metrics budget for the whole pool of metric data points in your environment, you can track available included metric data points against total reported metrics data points using these two metrics: (DPS) Available included metric data points for Full-Stack monitored hosts and (DPS) Total metric data points reported by Full-Stack monitored hosts. The example below shows data for a full day. At no time was the number of included metrics for this environment's metric pool (purple line) overspent.
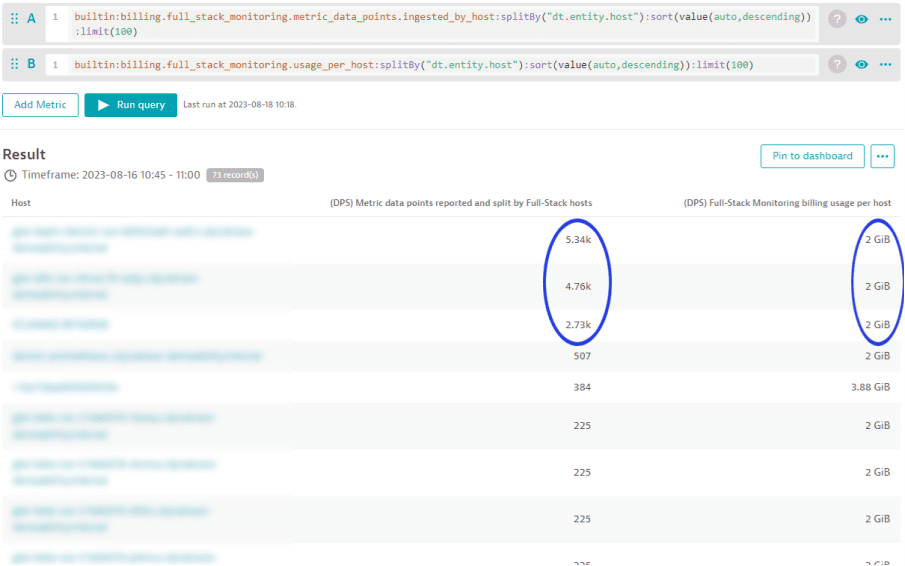
In cases where the number of included metrics for an environment's metric pool are overspent, the following analysis can help you to identify the hosts that are contributing to the overspending. Use the metric (DPS) Metric data points reported and split by Full-Stack monitored hosts for this analysis.
The example below shows that between 10:45 and 11:00, each of the first 3 hosts in the list reported far more than 2,000 metric data points. In the same period, each of these 3 hosts shows a memory-GiB-hour consumption of 2 GiB. Dynatrace offers 900 included custom metric data points for each GiB of host memory, calculated at 15-minute intervals. This means that the first 3 hosts contribute 1,800 (2*900) metric data points to the environment's pool of available data points. However these hosts consumed more data points than they contributed during the same time period.
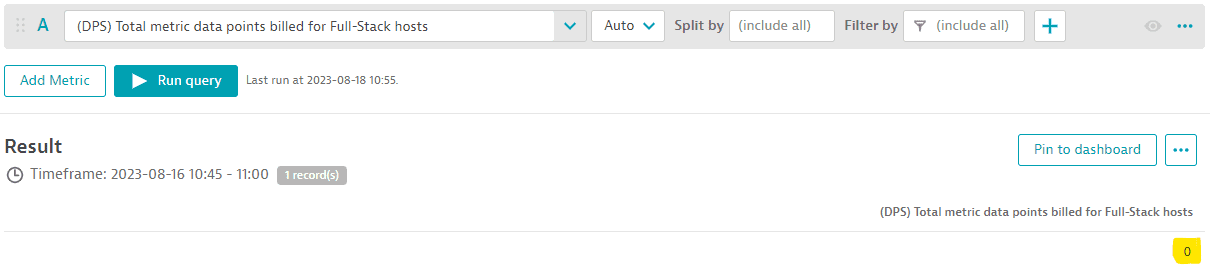
When using the metric (DPS) Total metric data points billed for Full-Stack monitored hosts from Custom Metrics Classic you can see that no overspending occurred for this environment's Full-Stack Monitoring metric pool between 10:45 and 11:00 because no metric data points were billed.
Infrastructure Monitoring
Dynatrace OneAgent can be configured for Infrastructure Monitoring mode, which provides comprehensive host monitoring for physical and virtual hosts.
In addition to all features of Foundation & Discovery, Infrastructure Monitoring also includes detailed process performance metrics, disk performance metrics, process-to-process network analysis, and per process memory analysis. Dynatrace Extensions can be enabled on hosts with Infrastructure Monitoring mode and may consume custom metric data points and Log Management and Analytics.
Host hours
The unit of measure for calculating consumption of host monitoring in Infrastructure Monitoring mode is a host-hour. Each instance of Dynatrace OneAgent installed and running on an operating system instance (deployed on either a physical or virtual machine) with Infrastructure Monitoring mode enabled consumes host hours. The longer that a host is monitored, the more host-hours you consume. Consumption is independent from a host's memory size.
Billing granularity for host-hour consumption
Dynatrace is built for elastic cloud-native environments where hosts and services are rapidly spun up and destroyed. Therefore, billing granularity for host-hour consumption is based on 15-minute intervals. When a host is monitored for fewer than 15 minutes in an interval, host-hour consumption is rounded up to 15 minutes before consumption is calculated.
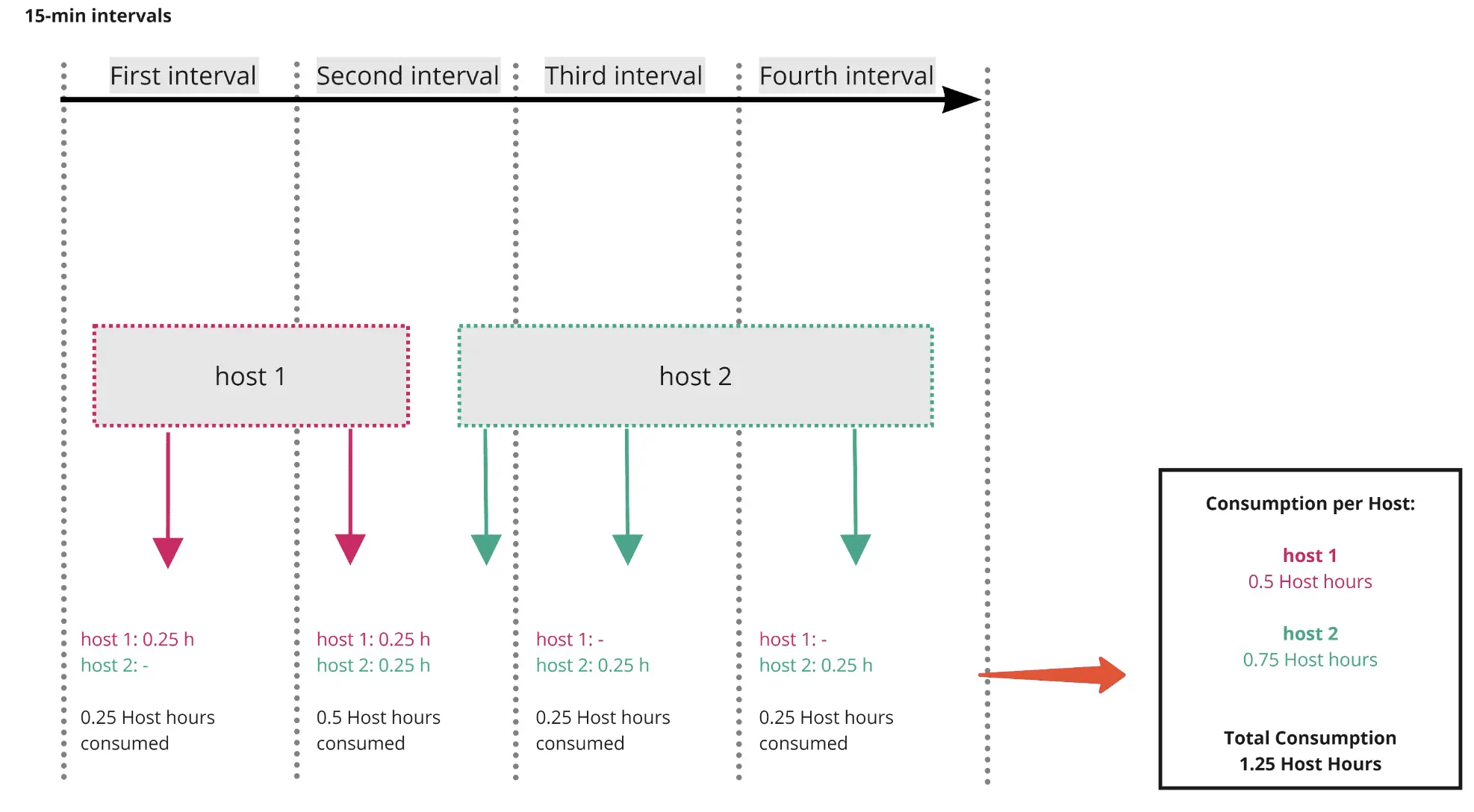
Figure 2 below illustrates how host-hour consumption per host is calculated.
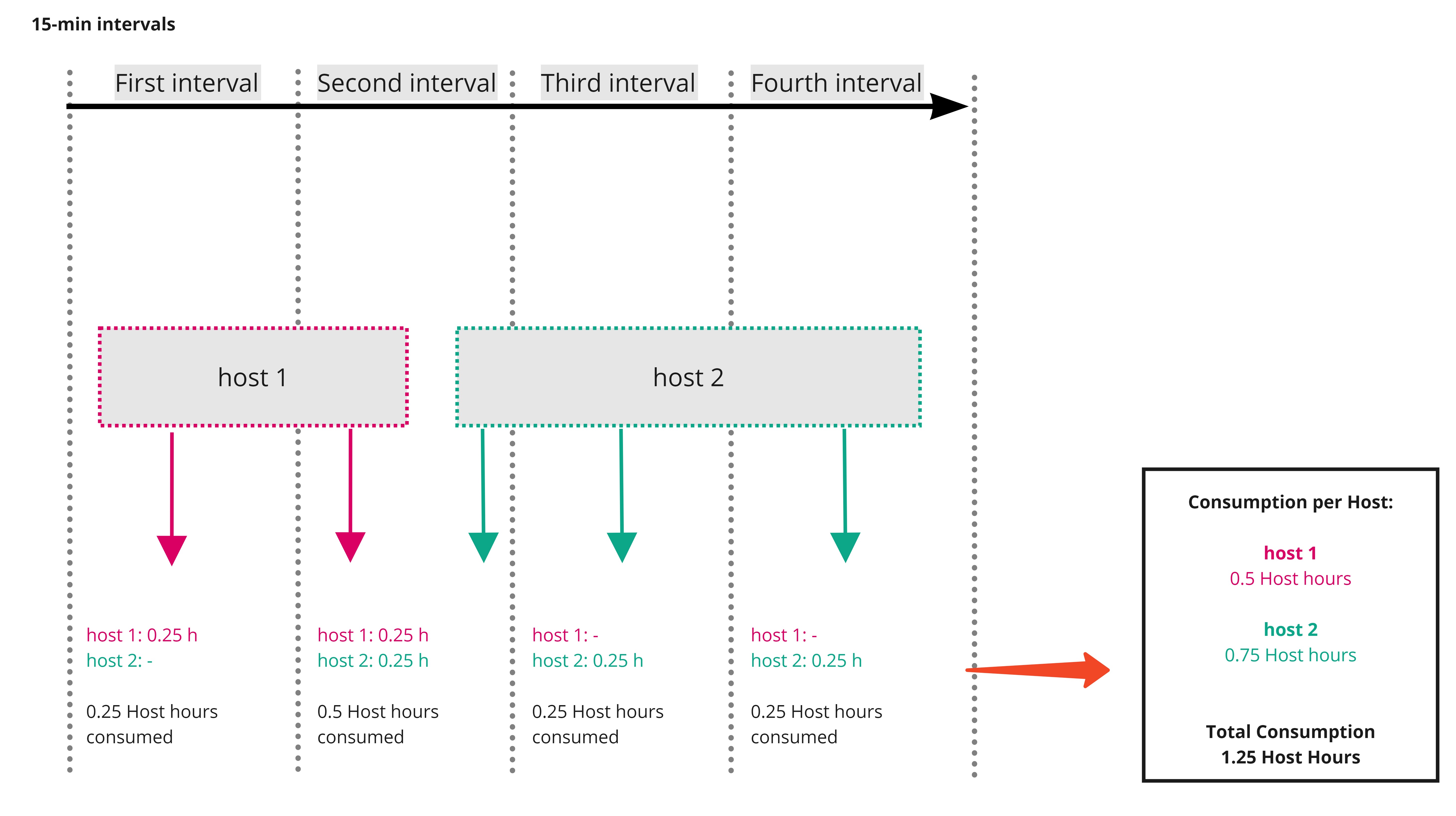
Figure 2. Host hour consumption per host, calculated at 15-minute intervals.
Metrics
Dynatrace Infrastructure Monitoring includes important built-in metrics. In addition to built-in metrics, Infrastructure monitoring includes a fixed number of custom metrics data points (we currently offer 1,500) for each 15-minute interval of monitoring per host. This equates to 100 custom metrics data points per minute at no additional cost. This "included" data point volume is available for all Infrastructure-monitored hosts in your environment. It applies only to metrics that originate at hosts that are monitored by OneAgent in Infrastructure Monitoring mode.
Looking at Figure 2 above, the included custom metric data point volume for the four 15-minute intervals is shown below.
Included custom metric data points calculation example
First 15-minute interval
1 (hosts monitored) × 1,500 (metric data points) = 1,500 Included custom metric data points
Second 15-minute interval
2 (hosts monitored) × 1,500 (metric data points) = 3,000 Included custom metric data points
Third 15-minute interval
1 (hosts monitored) × 1,500 (metric data points) = 1,500 Included custom metric data points
Fourth 15-minute interval
1 (hosts monitored) × 1,500 (metric data points) = 1,500 Included custom metric data points
How custom metric data points are consumed in Infrastructure Monitoring mode
Custom metric data-point consumption takes many forms. An equal number of custom metric data points can be consumed:
By a few high-resolution metrics or numerous low-resolution metrics.
Equally across multiple 15-minute intervals or all at once in a single minute.
By all Infrastructure-monitored hosts, a subset of all Infrastructure-monitored hosts, or a single infrastructure-monitored host.
Additional custom metric data points that your environment consumes (beyond those data points that are included with each Infrastructure-monitored host) are billed as Custom Metrics Classic.
Consumption details: Infrastructure
Dynatrace provides built-in usage metrics that help you understand and analyze your organization's consumption of Infrastructure Monitoring. To use these metrics, in Data Explorer, enter DPS in the Search field. These metrics are also available via the Environment API and in Account Management (Usage summary > Infrastructure Monitoring > Actions > View details).
Here is the list of metrics you can use to monitor the consumption details for Infrastructure Monitoring.
- (DPS) Infrastructure Monitoring billing usage
Key:
builtin:billing.infrastructure_monitoring.usageDimension: Count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Total number of host hours consumed in Infrastructure Monitoring mode.
- (DPS) Infrastructure Monitoring billing usage per host
Key:
builtin:billing.infrastructure_monitoring.usage_per_hostDimension: Host (
dt.entity.host)Resolution: 15 min
Description: Consumed host hours in Infrastructure Monitoring mode per host.
- (DPS) Total metric data points reported by Infrastructure hosts
Key:
builtin:billing.infrastructure_monitoring.metric_data_points.ingestedDimension: Count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Number of metric data points consumed by all Infrastructure-monitored hosts.
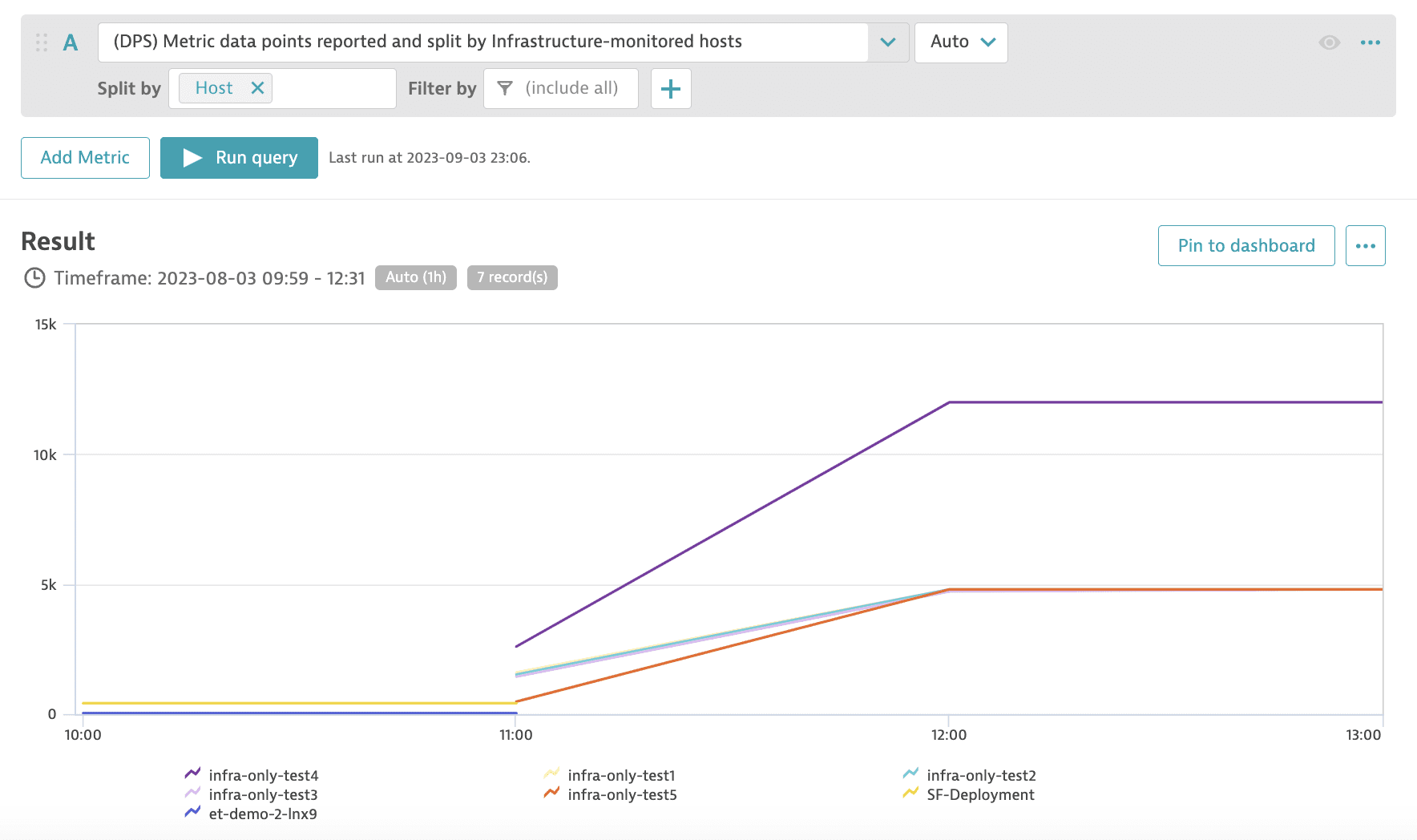
- (DPS) Metric data points reported and split by Infrastructure hosts
Key:
builtin:billing.infrastructure_monitoring.metric_data_points.ingested_by_hostDimension: Host (
dt.entity.host)Resolution: 15 min
Description: Number of metric data points, split by Infrastructure-monitored hosts.
- (DPS) Available included metric data points for Infrastructure-monitored hosts
Key:
builtin:billing.infrastructure_monitoring.metric_data_points.includedDimension: Count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Total number of included metric data points deductible from the metric data points reported by all Infrastructure-monitored hosts.
- (DPS) Consumed included metric data points for Infrastructure hosts
Key:
builtin:billing.infrastructure_monitoring.metric_data_points.included_usedDimension: Count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Number of consumed included metric data points for Infrastructure-monitored hosts.
- (DPS) Total metric data points billed for Infrastructure hosts
Key:
builtin:billing.custom_metrics_classic.usage.infrastructure_hostsDimension: Count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Number of metric data points billed for all Infrastructure-monitored hosts.
Monitor host-hour consumption
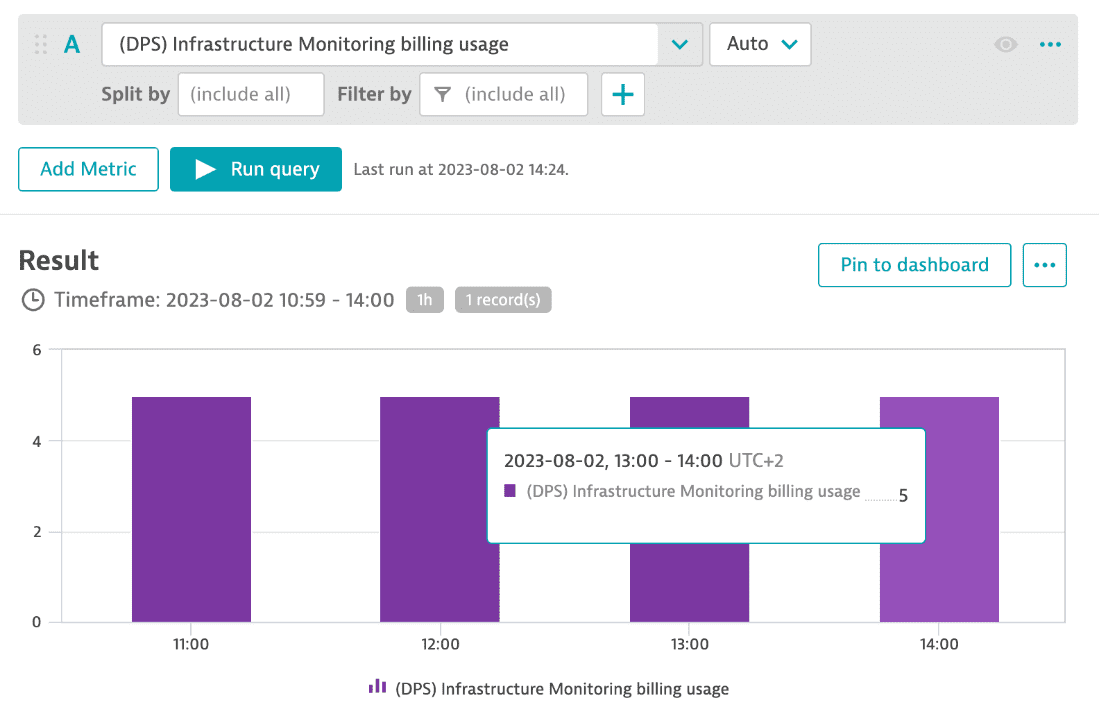
You can monitor the total host-hour consumption for different intervals (15 min, hour, day, or week) for any selected timeframe using the (DPS) Infrastructure Monitoring billing usage metric. The example below shows that 5 hosts were monitored, leading to total consumption of 5 host-hours for each hour.
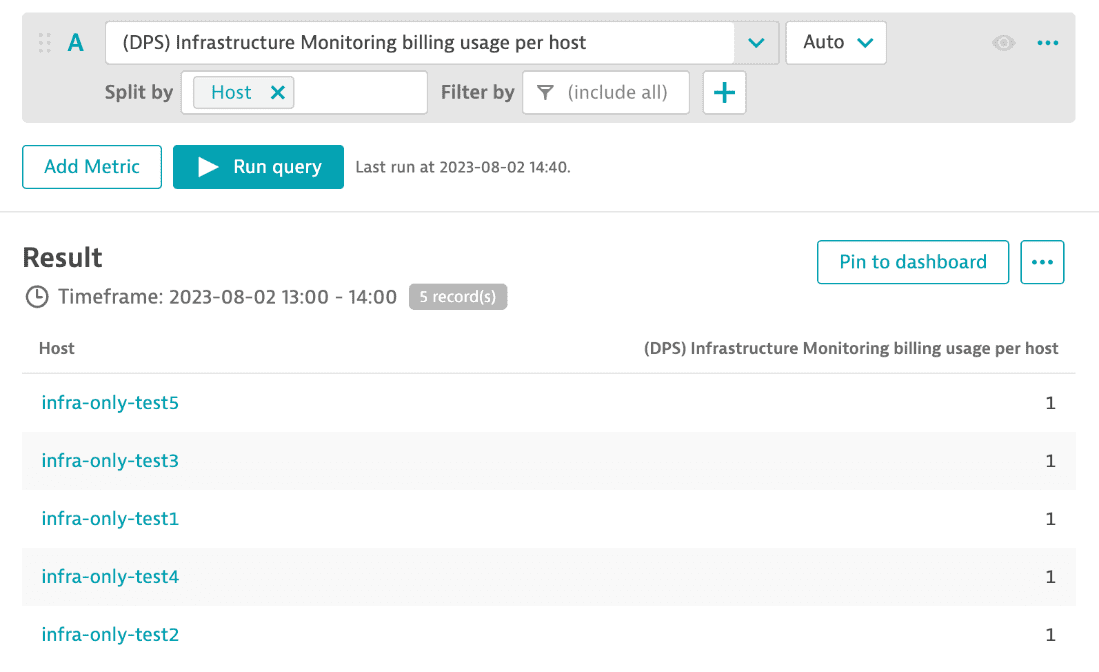
You can split the total host hour consumption using the metric (DPS) Infrastructure Monitoring billing usage per host. The example below shows the list of all hosts that reported consumption.
Monitor metric consumption for Infrastructure monitored hosts
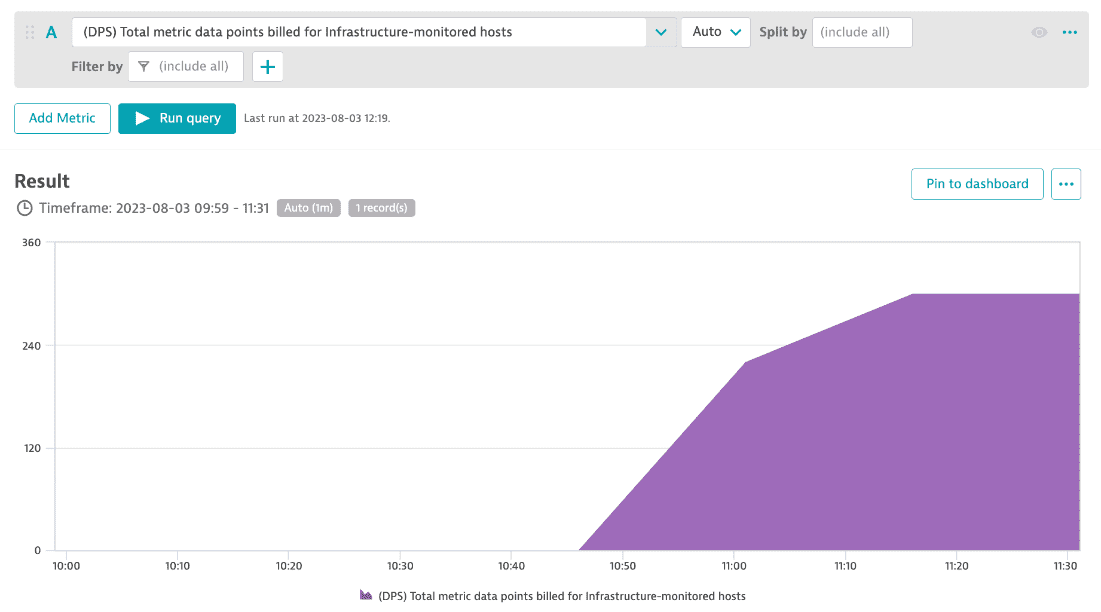
Use the metric (DPS) Total metric data points billed for Infrastructure hosts to monitor the number of metric data points that are billed for Infrastructure monitored hosts, as shown in the example below.
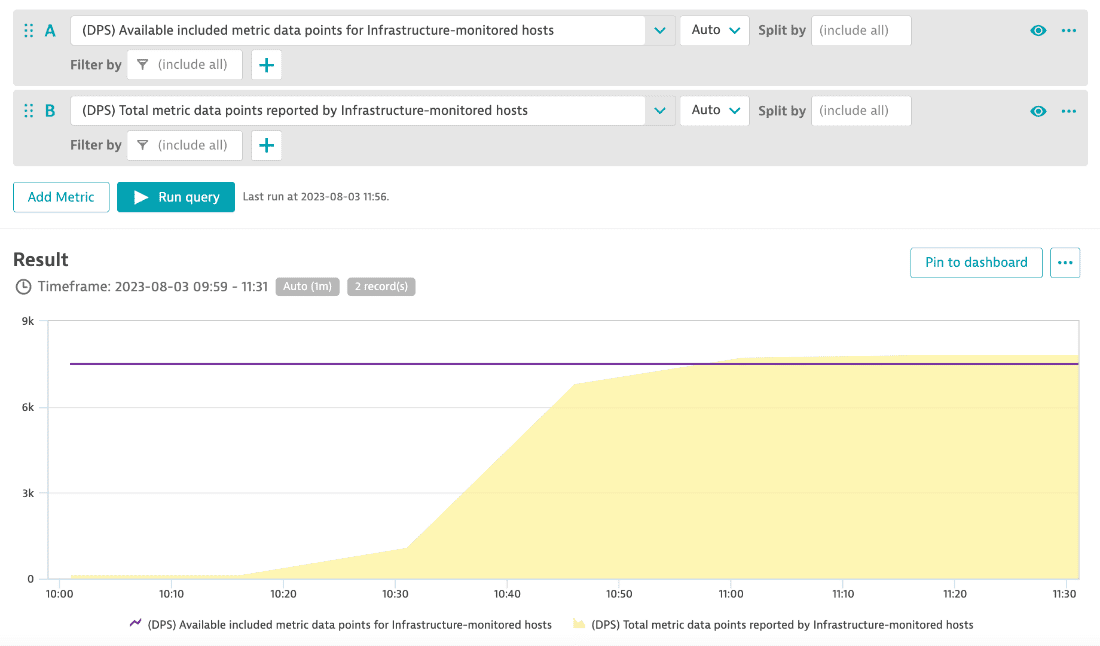
To manage your metrics budget, you can monitor the number of available included metric data points against the number of total consumed metrics data points using these two metrics: (DPS) Available included metric data points for Infrastructure hosts and (DPS) Total metric data points reported by Infrastructure hosts. The example below shows that more metric data points were consumed that were included with these Infrastructure monitored hosts.
You can use the metric (DPS) Metric data points reported and split by Infrastructure hosts to track the number of metric data points consumed per Infrastructure monitored host. The split view helps in discovering the hosts that consume the most metric data points. The example below shows that one of the Infrastructure monitored hosts reported significantly more metrics data points than the others.
Foundation & Discovery
Dynatrace OneAgent can be configured for Foundation & Discovery mode, which provides basic monitoring for your hosts (for example, host health, disk status, and OS service status). Unlike other tools that provide basic monitoring, Foundation & Discovery leverages core OneAgent features: discovery and topology.
Foundation & Discovery mode detects process-to-process communication and populates the Smartscape topology accordingly. This provides important clues for AIOps which is included with OneAgent, see Davis® AI automatic root cause analysis for details.
Broad deployment of Foundation & Discovery mode enables you to select the right monitoring mode for each of your hosts. A host’s criticality can be determined based on which processes, technologies, externally accessible services, and topological connections.
OneAgent in all modes also includes automated log ingestion, which consumes Log Management and Analytics.
Host hours
The unit of measure for calculating consumption of host monitoring in Foundation & Discovery mode is a host hour. Each instance of Dynatrace OneAgent installed and running on an operating system instance (deployed on either a physical or virtual machine) with Foundation & Discovery mode enabled consumes host hours. The longer that a host is monitored, the more host hours are consumed. Consumption is independent from a host's memory size.
While Foundation & Discovery and Infrastructure Monitoring both use host hours as their unit of measure for calculating monitoring consumption, Foundation & Discovery has a lower cost per host hour, reflecting its limited capabilities. For details on Dynatrace pricing, see your rate card, or speak to your Dynatrace account manager.
Billing granularity for host-hour consumption
Dynatrace is built for elastic cloud-native environments where hosts and services are rapidly spun up and destroyed. Therefore, billing granularity for host-hour consumption is based on 15-minute intervals. When a host is monitored for fewer than 15 minutes in an interval, host-hour consumption is rounded up to 15 minutes before consumption is calculated.
The image below illustrates how host-hour consumption per host, calculated at 15-minute intervals.
Metrics
Foundation & Discovery includes basic built-in metrics. Unlike Full-Stack and Infrastructure Monitoring, Foundation & Discovery doesn’t offer included custom metrics. For more information, see Infrastructure and Discovery monitoring modes.
Consumption details: Foundation & Discovery
Dynatrace provides built-in usage metrics that help you understand and analyze your organization's consumption of Foundation & Discovery. To use these metrics, in Data Explorer, enter DPS in the Search field. These metrics are also available via the Environment API and your Account Management portal (Usage summary > Foundation & Discovery > Actions > View details).
- (DPS) Foundation & Discovery billing usage
Key:
builtin:billing.foundation_and_discovery.usageDimension: count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Total number of host hours in Foundation & Discovery mode, counted in 15 min intervals.
- (DPS) Foundation & Discovery billing usage per host
Key:
builtin:billing.foundation_and_discovery.usage_per_hostDimension:
dt.entity.hostResolution: 15 min
Description: Host hours per host in Foundation & Discovery mode, counted in 15 min intervals.
- (DPS) Ingested metric data points for Foundation & Discovery
Key:
builtin:billing.foundation_and_discovery.metric_data_points.ingestedDimension: count
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Number of metric data points aggregated over all Foundation & Discovery monitored hosts.
- (DPS) Ingested metric data points for Foundation & Discovery per host
Key:
builtin:billing.foundation_and_discovery.metric_data_points.ingested_by_hostDimension:
dt.entity.hostResolution: 15 min
Description: Number of metric data points split per Foundation & Discovery monitored host.
Mainframe Monitoring
Dynatrace Mainframe Monitoring provides automatic end-to-end application performance monitoring for transactions, regions, and apps deployed on IBM z/OS. It includes distributed tracing, metrics, topology, and code-level insight for 30+ supported technologies.
With the DPS capability for Mainframe Monitoring:
You get flexibility in licensing for incremental monitoring rollouts (for example, you can start small and expand coverage over time).
You only pay for the active monitoring period (for example, downtimes are not charged).
You get cost transparency and budget management in Account Management.
The technical prerequisites for DPS are:
Dynatrace Cluster version 1.279+
- zRemote module version 1.265+
- zDC subsystem version 1.247+
A monitored Logical Partition (LPAR) is represented as a host in Dynatrace. The billing for monitoring an LPAR depends on the partition’s Million Service Unit (MSU) value and the duration of Dynatrace monitoring. An MSU is an IBM measurement of the amount of processing work an IBM Z mainframe can perform in one hour.
MSU hours
The unit of measure for Mainframe Monitoring is an MSU hour. Mainframe Monitoring consumption derives MSU hours based on the IBM Tailored Fit Pricing software consumption solution, retrieved per LPAR from SMF type 70 subtype 1 records (actual number of consumed MSUs).
The more MSUs an LPAR has, and the longer Dynatrace monitors it, the higher the MSU-hour consumption.
Billing granularity for MSU-hour consumption
The billing granularity for MSU-hour consumption is calculated in four 15-minute intervals per hour. If an LPAR is monitored for less than 15 minutes in an interval, MSU-hour consumption is rounded up to 15 minutes before consumption is calculated. The sum of MSU hours of all monitored LPARs represents the total consumption.
Distributed tracing
Mainframe Monitoring includes Dynatrace PurePath® distributed tracing. Dynatrace retains the total amount of ingested trace volume from your environment for ten days, with index-level access for 35 days.
Metrics
Mainframe Monitoring includes application performance monitoring and related built-in metrics, except custom metrics, which are measured in metric data points and billed separately. For example, custom JMX metrics consume metric data points. For complete details, see Custom Metrics Classic.
Consumption details: Mainframe
Dynatrace provides a usage metric that helps you understand and analyze your MSU-hour consumption. To use this metric, in Data Explorer, enter the following metric key or name in the Search field.
Alternatively, you can query this metric via the Environment API - Metrics API v2.
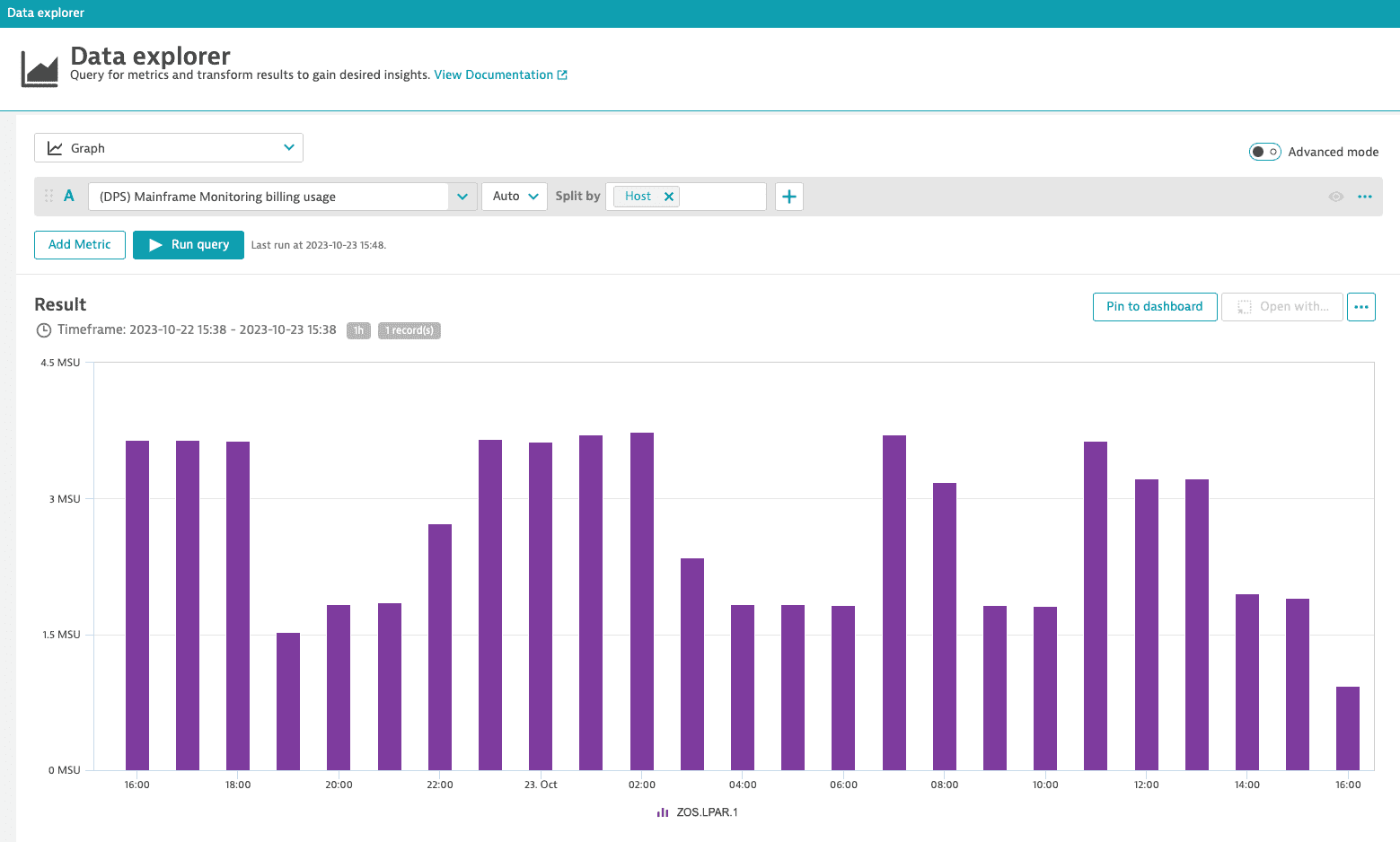
- (DPS) Mainframe Monitoring billing usage
Key:
builtin:billing.mainframe_monitoring.usageDimension: Host (
dt.entity.host)Resolution: 15 min
Description: Total number of MSU hours monitored, counted in 15 min intervals.
You can break down the MSU-hour consumption per LPAR. The example below shows all LPARs that contributed to the consumption in 1-hour intervals within the last 24 hours.
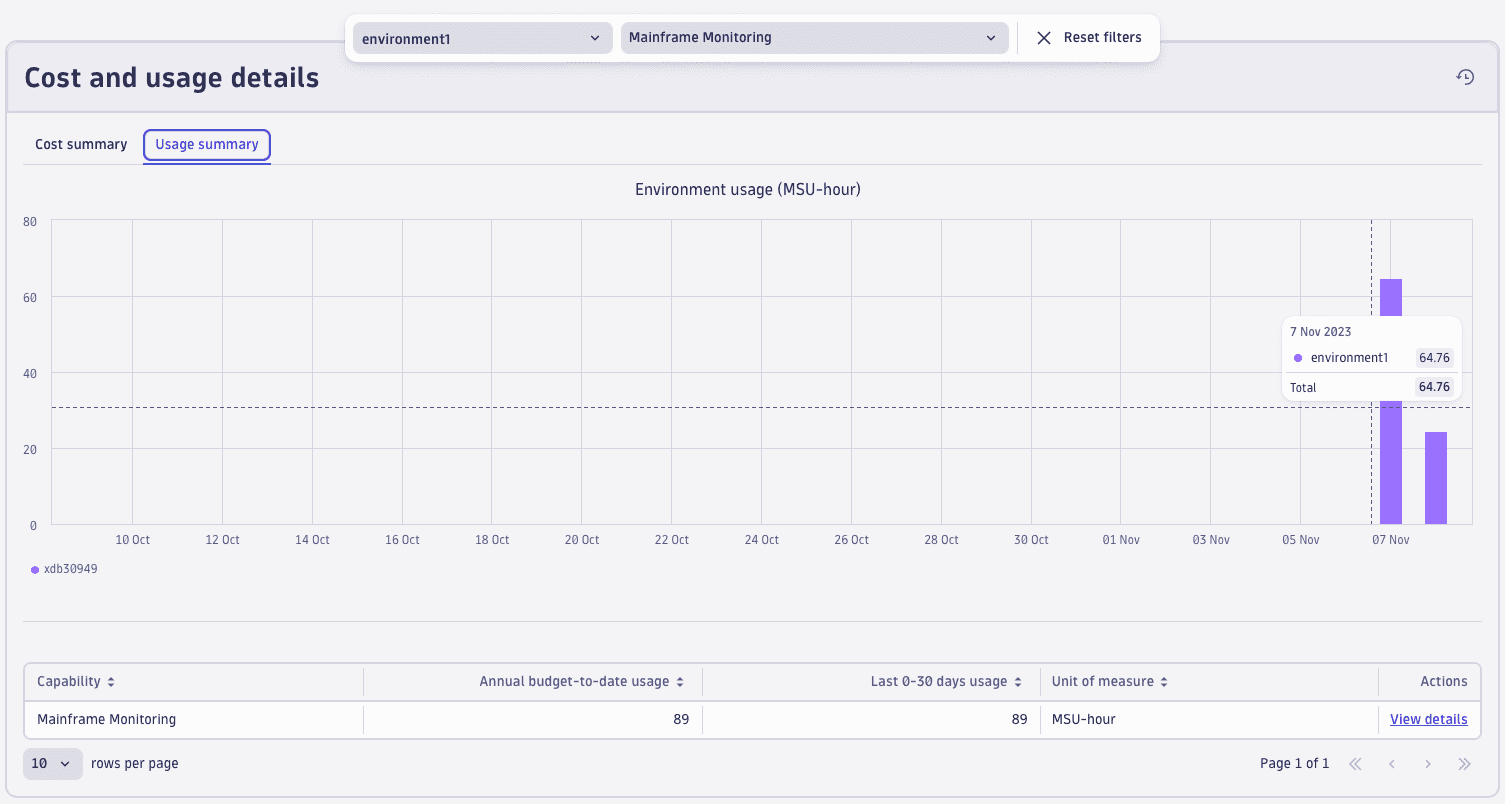
You can also view the usage metric in Account Management. Go to Account Management > Subscription > Overview > Cost and usage details > Usage summary and select the Mainframe Monitoring capability.
Consumption estimate: Mainframe
Use the IBM Sub-Capacity Reporting Tool (SCRT) report to estimate the required MSU-hour consumption per year.
- In Section C5, check the Reporting Period of the SCRT report. Typically, it contains one month of data.
- In Section N7, sum the Total MSU Consumed value for each LPAR to be monitored.
- If the reporting period is one month, multiply the Total MSU Consumed by 12 months to get annual consumption.
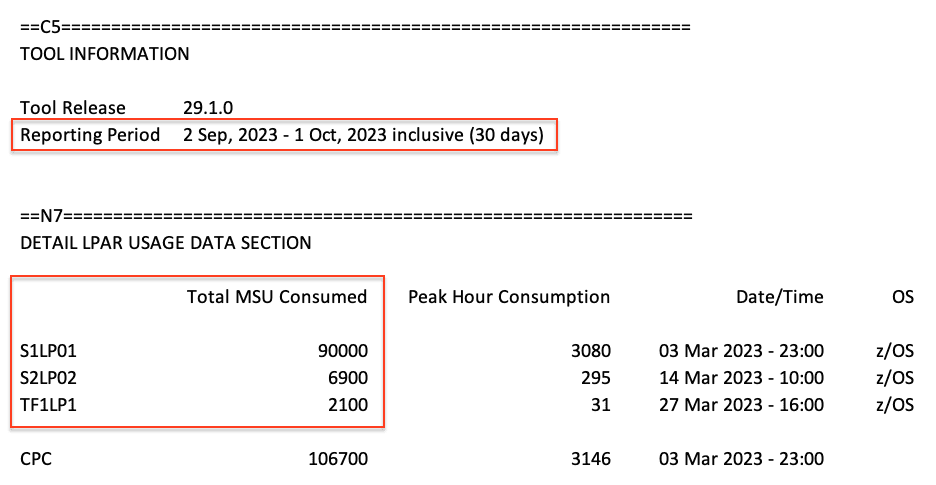
In this example, the three LPARs (S1LP01, S2LP02, and TF1LP1) consumed 99,000 MSU hours in September 2023.
Multiplied by 12 months, this equates to 1,188,000 MSU hours per year.
Notes:
This approach might not consider seasonal workload fluctuations, which can lead to deviations in actual consumption.
- Section N7 has been available since IBM SCRT version 25.2. It was released by IBM in December 2017.