Dynatrace OpenKit API methods
Dynatrace OpenKit offers a number of API methods that enable you to integrate OpenKit into your application. The sections below describe how to use each of these OpenKit methods.
Obtain an OpenKit instance
To obtain a new OpenKit instance, use DynatraceOpenKitBuilder.
endpointURLis the Dynatrace endpoint that OpenKit communicates with. You can find the endpoint URL in your custom application settings. See Instrument your application using Dynatrace OpenKit for more information.applicationIDis the unique identifier of the application. You can find the application ID in your custom application settings. See Instrument your application using Dynatrace OpenKit for more information.deviceIDis a unique identifier, which can be used to uniquely identify a device.
In addition to the mandatory parameters described above, the builder provides additional methods to further customize OpenKit. These include device-specific information like the operating system, manufacturer, or model ID.
SSL/TLS security
All OpenKit communication to the backend happens via HTTPS. By default, OpenKit expects valid server certificates. However, it is possible, if needed, to bypass certificate validation. You can configure a custom trust manager using the builder.
We do not recommend bypassing TLS/SSL server certificate validation, since this allows man-in-the-middle attacks.
Enable verbose logging
By default, OpenKit uses a logger implementation that logs to stdout. If the default logger is used, you can enable verbose logging via DynatraceOpenKitBuilder. When the verbose mode is enabled, info and debug messages are logged.
You can also configure a custom logger. For details, see Dynatrace OpenKit logging.
Initialize OpenKit
When obtaining an OpenKit instance from the builder, the instance starts an automatic initialization phase. By default, initialization is performed asynchronously.
There might be situations when you need to ensure that initialization is completed before proceeding with the program logic, for example, in case of short-lived applications where a valid init and shutdown cannot be guaranteed. For such applications, OpenKit allows to wait for the initialization in two ways:
- With timeout: The calling threads waits a given amount of time for OpenKit to initialize. The method returns
falsein case the timeout expired or a shutdown was performed in the meantime andtrueto indicate successful initialization. - Without timeout: The calling thread blocks until OpenKit is initialized. In case of misconfiguration this might block the calling thread indefinitely. The return value indicates whether the OpenKit instance has been initialized or a shutdown was performed meanwhile.
In addition, OpenKit enables you to verify whether or not it's been initialized.
Create a session
You can create a new session using the OpenKit instance obtained from the builder. When creating a new session, you can also provide an IP address.
If a valid IPv4 or IPv6 address is provided, it is assigned to the session.
If no IP address or an invalid IP address is provided, the IP address of the session is auto-detected and assigned on the server side.
Tag specific users
You can tag the user assigned to a session. This enables you to search and filter specific user sessions and analyze individual user behavior over time in the backend. See User tagging for more details.
When the user opt-in mode is enabled for your application, it might affect user tagging and reporting of custom events, user actions, values, and errors. The exact data types not reported to Dynatrace depend on the data collection level set by a particular user. For details, refer to Data collection levels.
Finish a session
When a session is no longer needed, you should end it explicitly. Although all open sessions are automatically ended when OpenKit is shut down, it's highly recommended to manually end sessions that are no longer in use.
Report a crash
You can report unexpected application crashes on a session. The crash details are sent immediately after you've reported a crash.
Create custom and child actions
You can define and report custom actions. After you create a custom action, you can add a child action to it or enhance an action with additional information before finally closing it. You should create custom actions from a session and child actions from a custom action.
The maximum duration of a user action in custom apps is 10 minutes. When a user action takes longer than this, such an action is discarded and not reported to Dynatrace.
There's no limit on the number of child actions attached to a custom action. However, note that you can have only one level of child actions—you can't create a child action for another child action (child actions can't have their own child actions). Also, refer to User session structure for individual user.
Child actions are not displayed on the user session details page, but you can view them on the waterfall analysis page for a custom action to which these child actions are attached.
When the user opt-in mode is enabled for your application, it might affect user tagging and reporting of custom events, user actions, values, and errors. The exact data types not reported to Dynatrace depend on the data collection level set by a particular user. For details, refer to Data collection levels.
End an action
To record accurate timing information for actions, you should leave actions once they're finished.
Cancel an action
Canceling an action is similar to leaving an action, except that the action is discarded and is not sent to Dynatrace. Open child objects, like child actions and web request tracers, are discarded as well. Child objects that have been closed previously are sent to the backend and might be processed, depending on the event type.
Report an event
You can report named events on actions.
If you want to report standalone events with lots of additional information, see Report a business event.
When the user opt-in mode is enabled for your application, it might affect user tagging and reporting of custom events, user actions, values, and errors. The exact data types not reported to Dynatrace depend on the data collection level set by a particular user. For details, refer to Data collection levels.
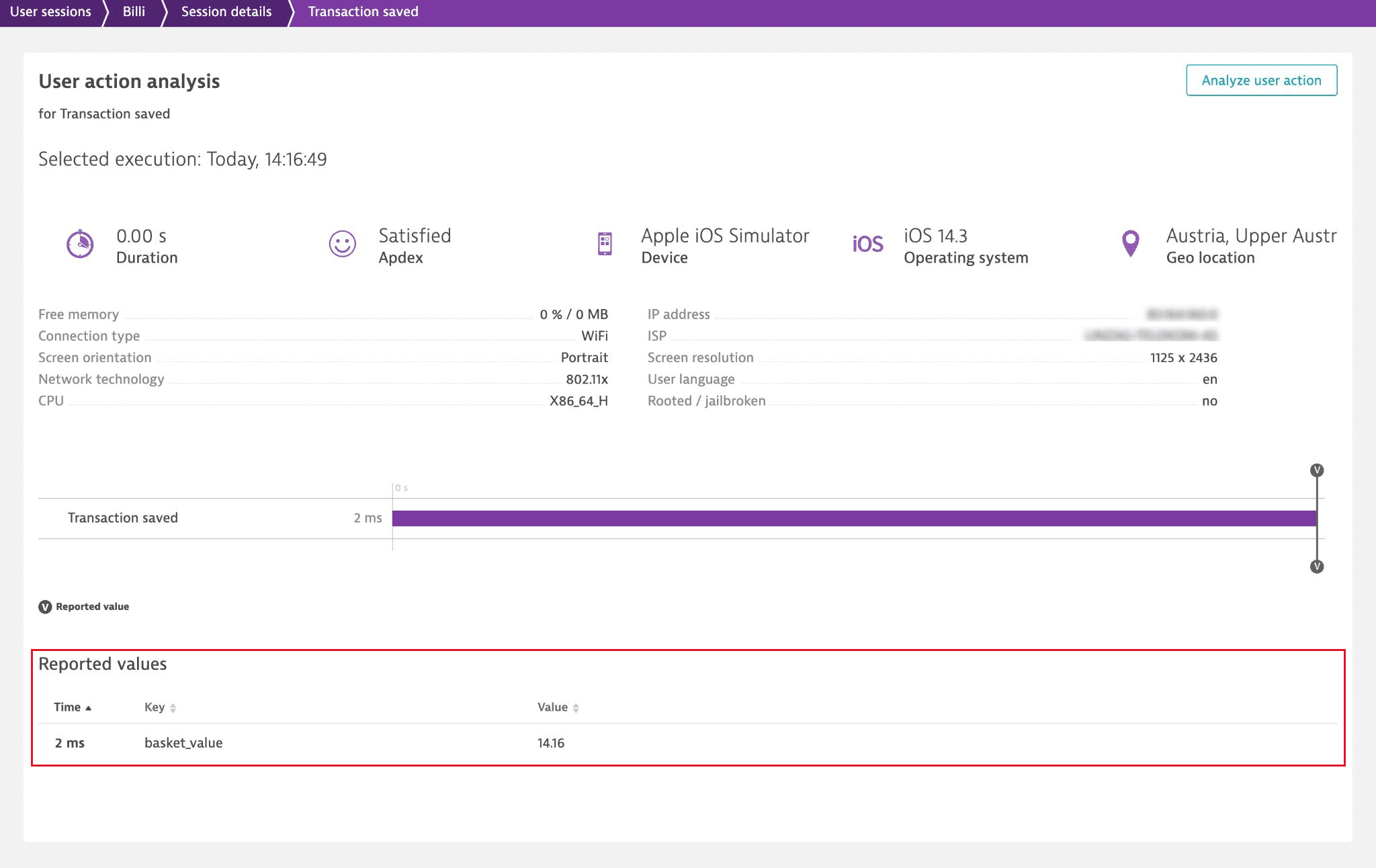
Report a value
The reportValue method allows you to report key-value pairs of metadata that you can later view in the Dynatrace web UI and convert into user action and user session properties. The reported values must be part of a user action.
You can report values of the following data types:
32-bit integer
64-bit integer
Double
String
To view the reported values in Dynatrace, go to the details of the user action that should contain that metadata and scroll down to the Reported values section.
To add action and session properties based on the reported values and then use these properties to create powerful queries, segmentations, and aggregations, see Define user action and user session properties for custom applications.
When the user opt-in mode is enabled for your application, it might affect user tagging and reporting of custom events, user actions, values, and errors. The exact data types not reported to Dynatrace depend on the data collection level set by a particular user. For details, refer to Data collection levels.
Report an error
You can report an error including its name (errorName) and error code (errorCode).
You can also report the following additional information on the error:
- required
errorName—The human-readable name of the error. - optional
causeName—The cause leading to the reported error, for example, the exception's class name. - optional
causeDescription—The description of the cause leading to the error, for example, the exception's description. - optional
stackTraceorcauseStackTrace—The stack trace of the cause leading to the error.
The code snippet below shows how to report errors with additional information.
OpenKit Java and OpenKit .NET offer a convenience API to directly report caught exceptions, as demonstrated in the example below.
When the user opt-in mode is enabled for your application, it might affect user tagging and reporting of custom events, user actions, values, and errors. The exact data types not reported to Dynatrace depend on the data collection level set by a particular user. For details, refer to Data collection levels.
Report a business event
Dynatrace SaaS version 1.253+
With sendBizEvent, you can report business events. These are standalone events, as Dynatrace sends them separately from user actions or user sessions.
Business events are only captured for monitored sessions. When OpenKit isn't initialized or a session is excluded from monitoring due to cost and traffic control, business events are not reported for such sessions. Note that this behavior might be subject to change in the future, potentially allowing business events to be sent to Dynatrace regardless of session monitoring.
For additional details on business events, refer to Business Analytics.
Trace web requests
One of the most powerful OpenKit features is web request tracing. When the application starts a web request, for example, HTTP GET, a special tag can be attached to the header. This header allows Dynatrace to correlate actions with a server-side distributed trace. An example is shown below.
Configure data privacy
You can dynamically adjust data privacy settings and build your custom applications in compliance with data protection laws and regulations. The privacy API methods allow you to dynamically change the data collection level and activate or deactivate crash reporting.
Data collection levels
The table below describes the available data collection levels and shows whether user tags and custom user actions, events, values, and errors are reported for a particular level.
| Level | Description | User tags, custom events, and custom values | Custom user actions and errors |
|---|---|---|---|
Off Monitoring data is not sent | No personal data is sent; all identifiers are randomized on every launch.1 | ||
Performance Only performance, automatically captured data is sent | No personal data is sent; all identifiers are randomized on every launch. | ||
User behavior Performance data and user data is sent | Personal data is sent; OneAgent recognizes and reports users who revisit in the future.2 |
A single Loading <App> event is sent to track the number of users that opted out.
If you haven't configured user tagging and custom event or value reporting, the User behavior level works similarly to the Performance level.
Crash reporting levels
The following crash reporting levels are available.
| Level name | Crash reporting | Use this level when… |
|---|---|---|
Off |
| You don't need to collect crash reports. |
Opt out crashes |
| The user of your application has disallowed the collection of crash reports. |
Opt in crashes default |
| The user of your application has allowed the collection of crash reports. |
Set data collection and crash reporting levels
The code examples below show you how to work with the API:
Terminate an OpenKit instance
When an OpenKit instance is no longer needed, for example, when the application using OpenKit is shut down, you can clear the obtained instance by invoking. A call to shutdown blocks the calling thread up to 10 seconds, while the OpenKit flushes data that hasn't been transmitted yet to the backend.